Parallel data providers are an approach used to enhance the efficiency of data processing by running multiple data retrieval tasks concurrently. This technique is particularly useful in scenarios where data needs to be fetched from multiple sources or where data retrieval is time-consuming. Here are some key aspects of parallel data providers:
1. Concept and Benefits
- Concurrent Execution: By running data providers in parallel, tasks can be executed simultaneously, significantly reducing the overall time required to collect data.
- Improved Performance: Parallel data providers can leverage multi-core processors and distributed systems to handle large datasets more effectively.Scalability: As data requirements grow, parallel processing can scale to accommodate increased demand without a proportional increase in processing time.
2. Implementation Strategies
- Multithreading: This involves creating multiple threads within a single process, where each thread handles a separate data provider.
- Multiprocessing: This approach uses multiple processes, each with its own memory space, to run data providers. It can be more efficient for CPU-bound tasks.
- Asynchronous Programming: Using asynchronous I/O operations allows the program to continue executing other tasks while waiting for data retrieval to complete, making it suitable for I/O-bound tasks.
3. Tools and Libraries
- Python:
- Threading: threading module for multithreading.
- Multiprocessing: multiprocessing module for multiprocessing.
- Asyncio: asyncio module for asynchronous programming.
- Java:
- ExecutorService: Part of the java.util.concurrent package for managing thread pools.
- ForkJoinPool: For dividing tasks into smaller sub-tasks and processing them in parallel.
- JavaScript:
- Promises: For handling asynchronous operations.
- Web Workers: For running scripts in background threads.
- Frameworks:
- Apache Spark: For large-scale data processing with parallel execution capabilities.
- Dask: A parallel computing library in Python for analytics.
4. Challenges and Considerations
- Concurrency Control: Managing access to shared resources to avoid conflicts and ensure data consistency.
- Error Handling: Implementing robust error handling to manage failures in one or more data providers without affecting the overall process.
- Resource Management: Efficiently managing system resources such as CPU, memory, and I/O bandwidth to prevent bottlenecks.
- Debugging and Testing: Debugging parallel code can be more complex, requiring tools and techniques to monitor and trace execution.
5. Use Cases
- Web Scraping: Collecting data from multiple websites simultaneously.
- APIs: Fetching data from multiple APIs in parallel to reduce latency.
- Data Aggregation: Combining data from various sources like databases, files, and external services.
Example in Python Using asyncio
Here’s a simple example of running multiple data providers in parallel using the asyncio library in Python:
import asyncio
async def fetch_data(provider):
# Simulate a network request with asyncio.sleep
await asyncio.sleep(1)
return f"Data from {provider}"
async def main():
providers = ['Provider 1', 'Provider 2', 'Provider 3']
tasks = [fetch_data(provider) for provider in providers]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
for result in results:
print(result)
# Run the main function
asyncio.run(main())
In this example, fetch_data simulates a network request, and asyncio.gather runs these tasks concurrently, fetching data from multiple providers in parallel.

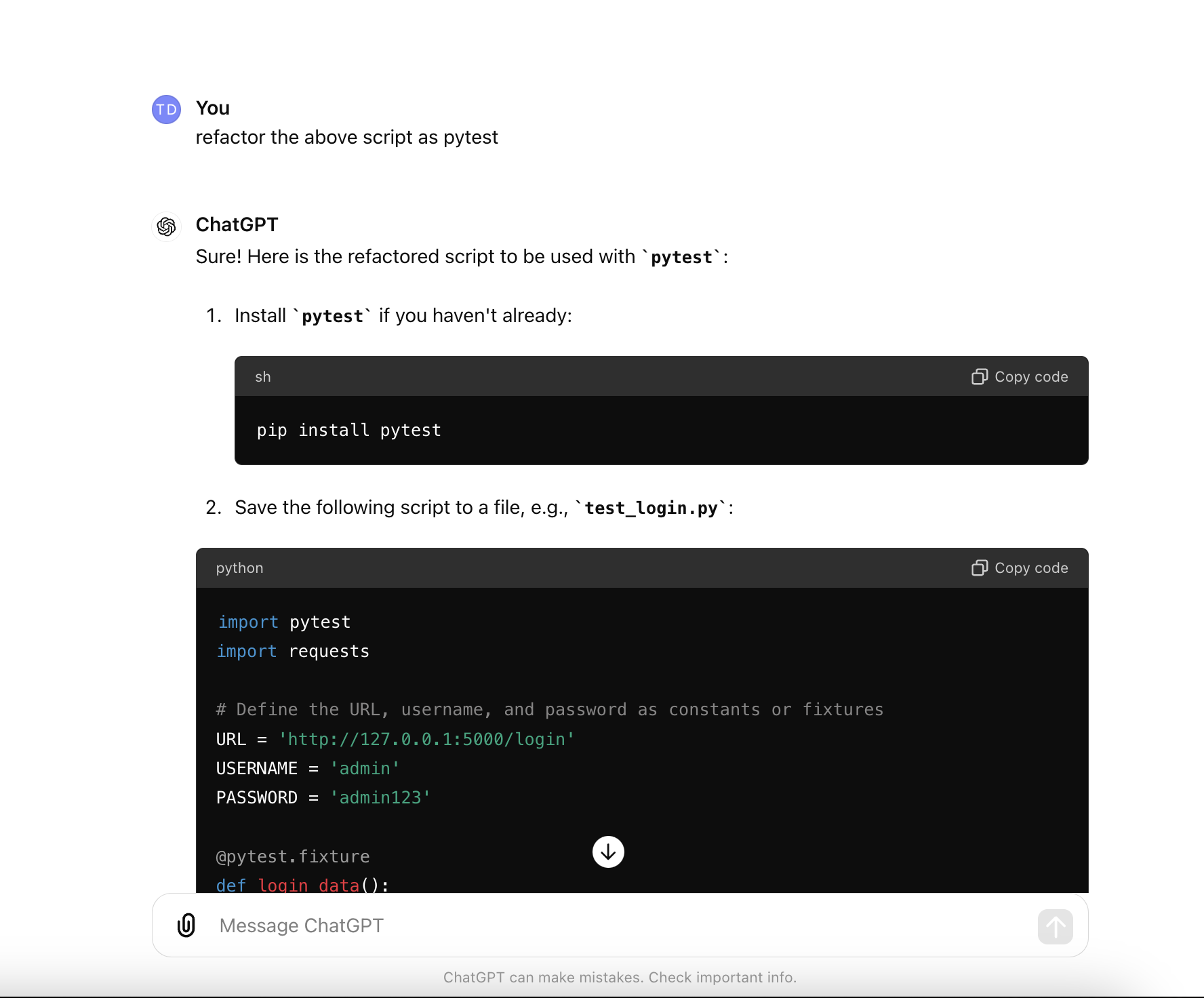 AI write script - Data-Driven Mongodb
AI write script - Data-Driven Mongodb