How AI (Chatgpt) to write automation test script with Data-Driven Mongodb
Overview
Here is my self assignment, to work with Chatgpt to test the way it suggested us to write automation test for API as bellow:
I have the curl command to test Login and get token.
curl --location 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin123"
}'
and the response data will be like:
{
"data": {
"token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ImFkbWluIn0.vb1PIGc2ZoxpcJ0sPAYCjc4-D1o3nCzCyNZiWWYZy3E"
},
"message": "OK"
}
1 - Request ChatGPT write Python script to cover API test
And Here is the way I communicated with Chatgpt to complete my self-assignment :)
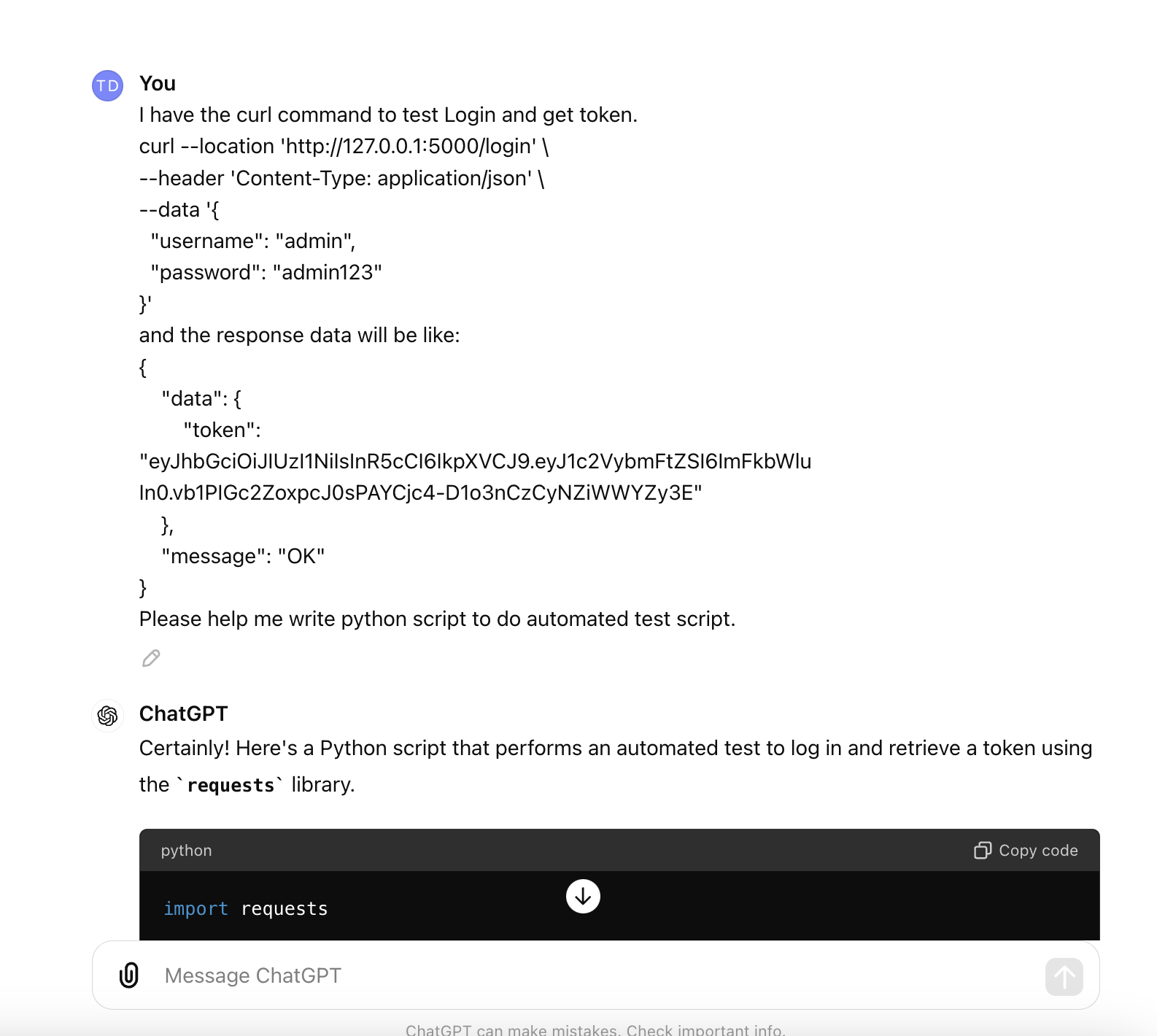
Here is the content of suggested script from Chatgpt:
import requests
def test_login(url, username, password):
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
data = {
"username": username,
"password": password
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data)
if response.status_code == 200:
response_data = response.json()
if 'data' in response_data and 'token' in response_data['data']:
token = response_data['data']['token']
print(f"Login successful. Token: {token}")
return token
else:
print("Token not found in response.")
return None
else:
print(f"Login failed. Status code: {response.status_code}")
return None
# Usage
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login'
username = 'admin'
password = 'admin123'
test_login(url, username, password)
And Chatgpt also explained us the meaning of scripts and the ways we should setup to make sure the scripts will be executed successfully as below:

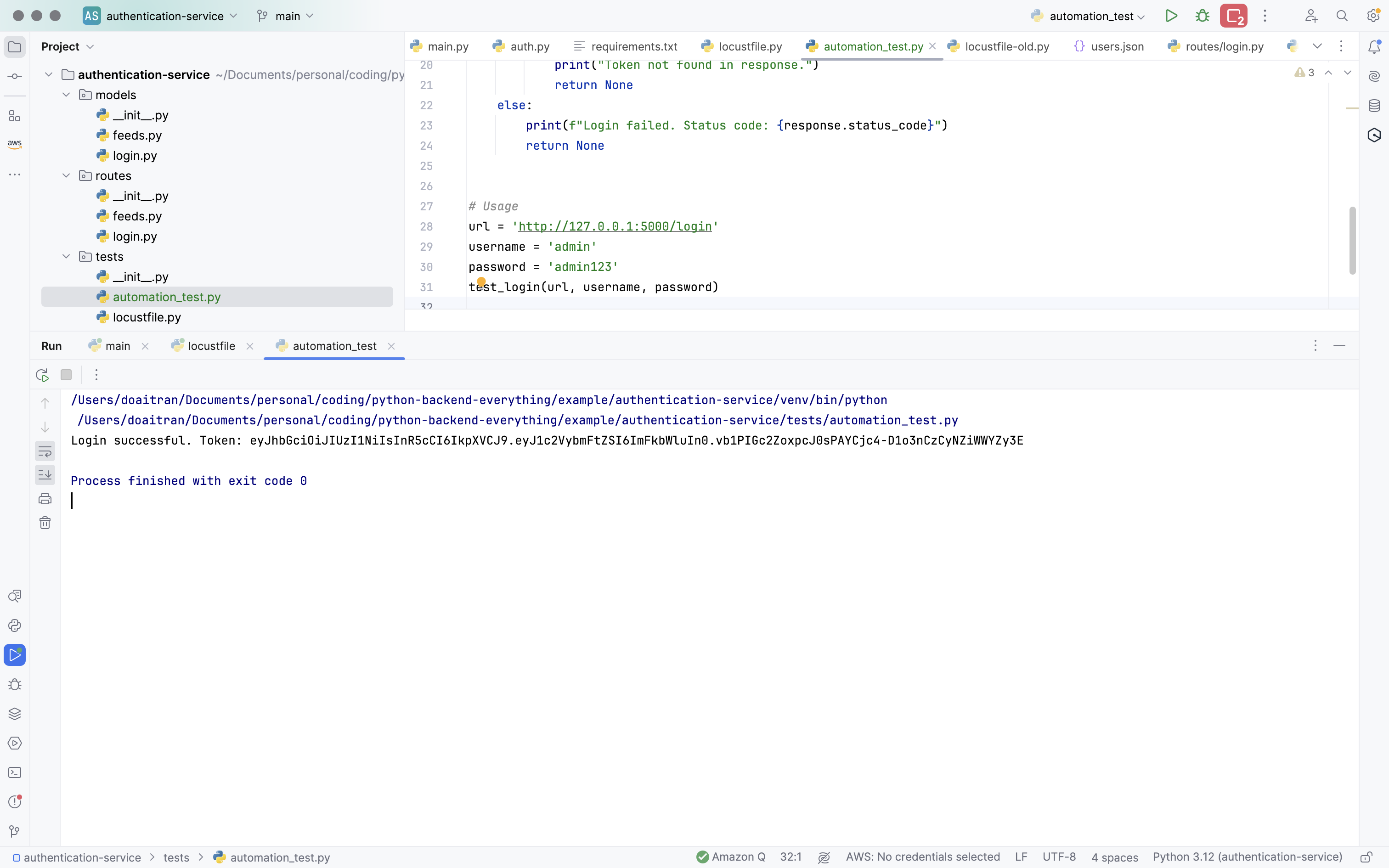
2 - Test the scripts
However, we should NOT use all data that Chatgpt suggested us, we will modify it how it is more useful, maintainable, clean-code, … test scripts.
3 - Request Chatgpt refactor code using Pytest test framework:
One the other hand, we can request chatgpt refactor code as Pytest with request as below:
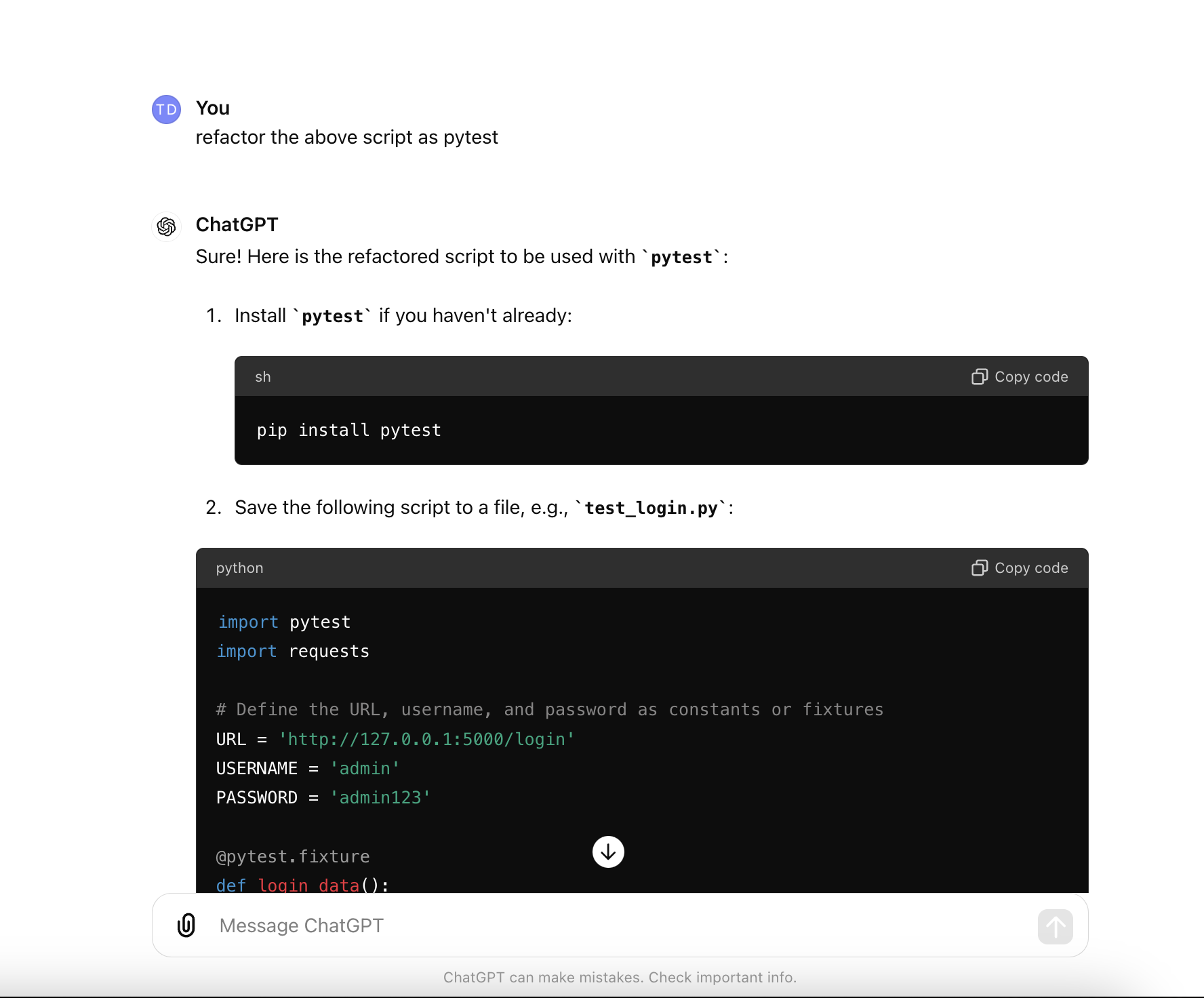
Content of the new version of test script:
We can get that Chatgpt also suggested me 2 test cases, it is quite good and useful for us.
import pytest
import requests
# Define the URL, username, and password as constants or fixtures
URL = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login'
USERNAME = 'admin'
PASSWORD = 'admin123'
@pytest.fixture
def login_data():
return {
"username": USERNAME,
"password": PASSWORD
}
@pytest.fixture
def headers():
return {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
def test_login_success(headers, login_data):
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=login_data)
assert response.status_code == 200, f"Expected status code 200, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'data' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'data' key"
assert 'token' in response_data['data'], "Response JSON does not contain 'token' in 'data' key"
token = response_data['data']['token']
assert token is not None, "Token should not be None"
print(f"Login successful. Token: {token}")
def test_login_failure(headers):
# Test with wrong credentials
wrong_data = {
"username": "wrong_user",
"password": "wrong_pass"
}
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=wrong_data)
assert response.status_code == 401, f"Expected status code 401, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'message' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'message' key"
assert response_data['message'] == 'Unauthorized', f"Expected message 'Unauthorized', but got {response_data['message']}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main()
As suggestions from Chatgpt, we have to install the essential library in our python project.
pip install pytest
From the response, we also have the explanation from Chatgpt as bellow:

And here is the result, when I tested the new version of test script that Chatgpt suggested me
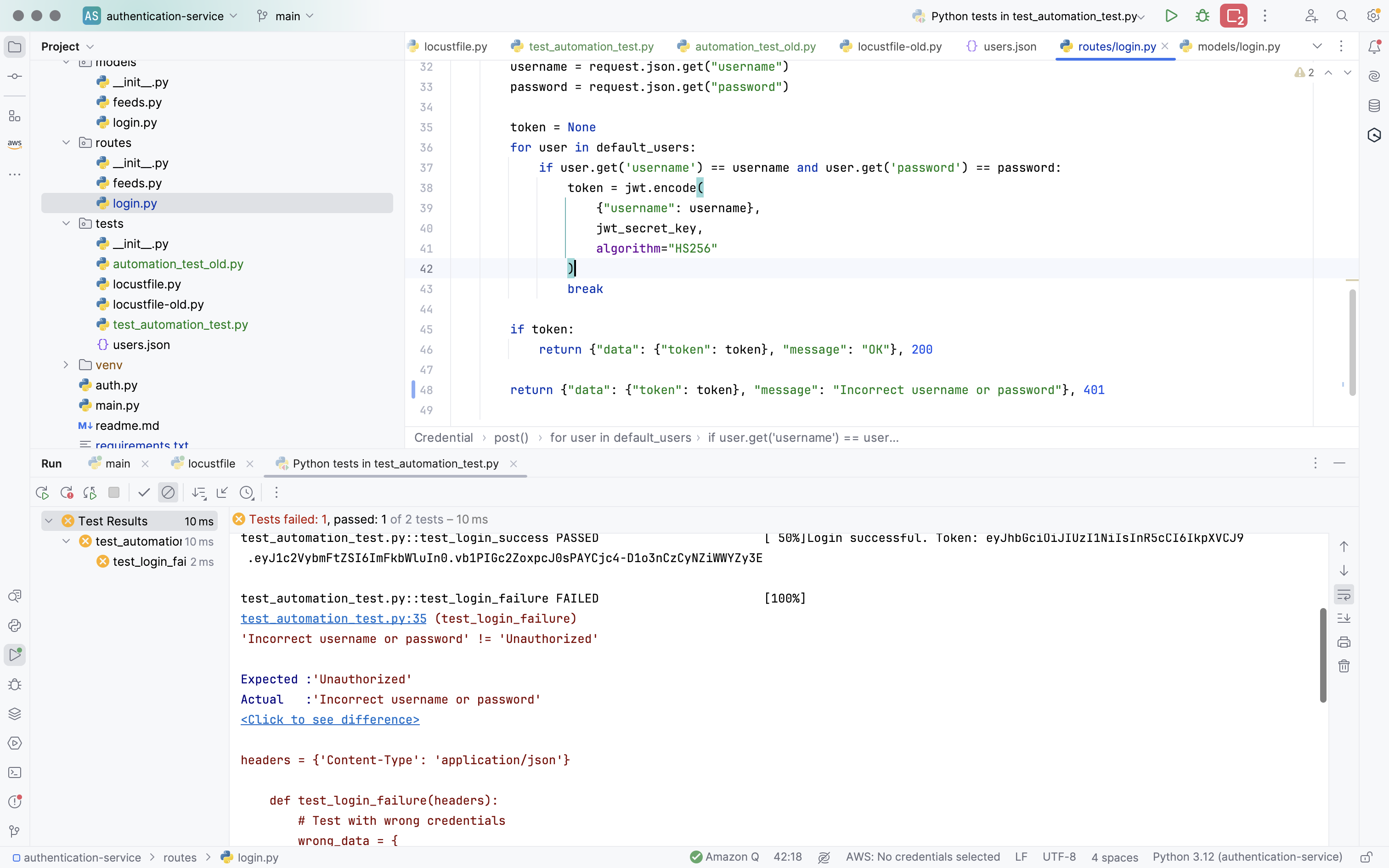
The first test case is PASSED, however the second test case is FAILED. Actually, my example service has the contract API as:
- The request login with failed credential will be received status code: 500 in response message
- And body message:
{
"data": {
"token": null
},
"message": "Incorrect username or password"
}
We have 2 options:
- we have to adjust and refactor this code, how it reflect correct our current contract
- or we request Chatgpt help us refactor code.
I tried to request chatgpt help me refactor code more
Could you help me refactor the test script, how it reflects to current correct response in test_login_failure, it should be:
- status code: 401
- response message
{
"data": {
"token": null
},
"message": "Incorrect username or password"
}
Content of new version script:
import pytest
import requests
# Define the URL, username, and password as constants or fixtures
URL = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login'
USERNAME = 'admin'
PASSWORD = 'admin123'
@pytest.fixture
def login_data():
return {
"username": USERNAME,
"password": PASSWORD
}
@pytest.fixture
def headers():
return {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
def test_login_success(headers, login_data):
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=login_data)
assert response.status_code == 200, f"Expected status code 200, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'data' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'data' key"
assert 'token' in response_data['data'], "Response JSON does not contain 'token' in 'data' key"
token = response_data['data']['token']
assert token is not None, "Token should not be None"
print(f"Login successful. Token: {token}")
def test_login_failure(headers):
# Test with wrong credentials
wrong_data = {
"username": "wrong_user",
"password": "wrong_pass"
}
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=wrong_data)
assert response.status_code == 401, f"Expected status code 401, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'data' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'data' key"
assert 'token' in response_data['data'], "Response JSON does not contain 'token' in 'data' key"
assert response_data['data']['token'] is None, "Expected token to be None"
assert 'message' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'message' key"
assert response_data['message'] == 'Incorrect username or password', f"Expected message 'Incorrect username or password', but got {response_data['message']}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main()
And I test again the test scripts. And it is working well as we expected.
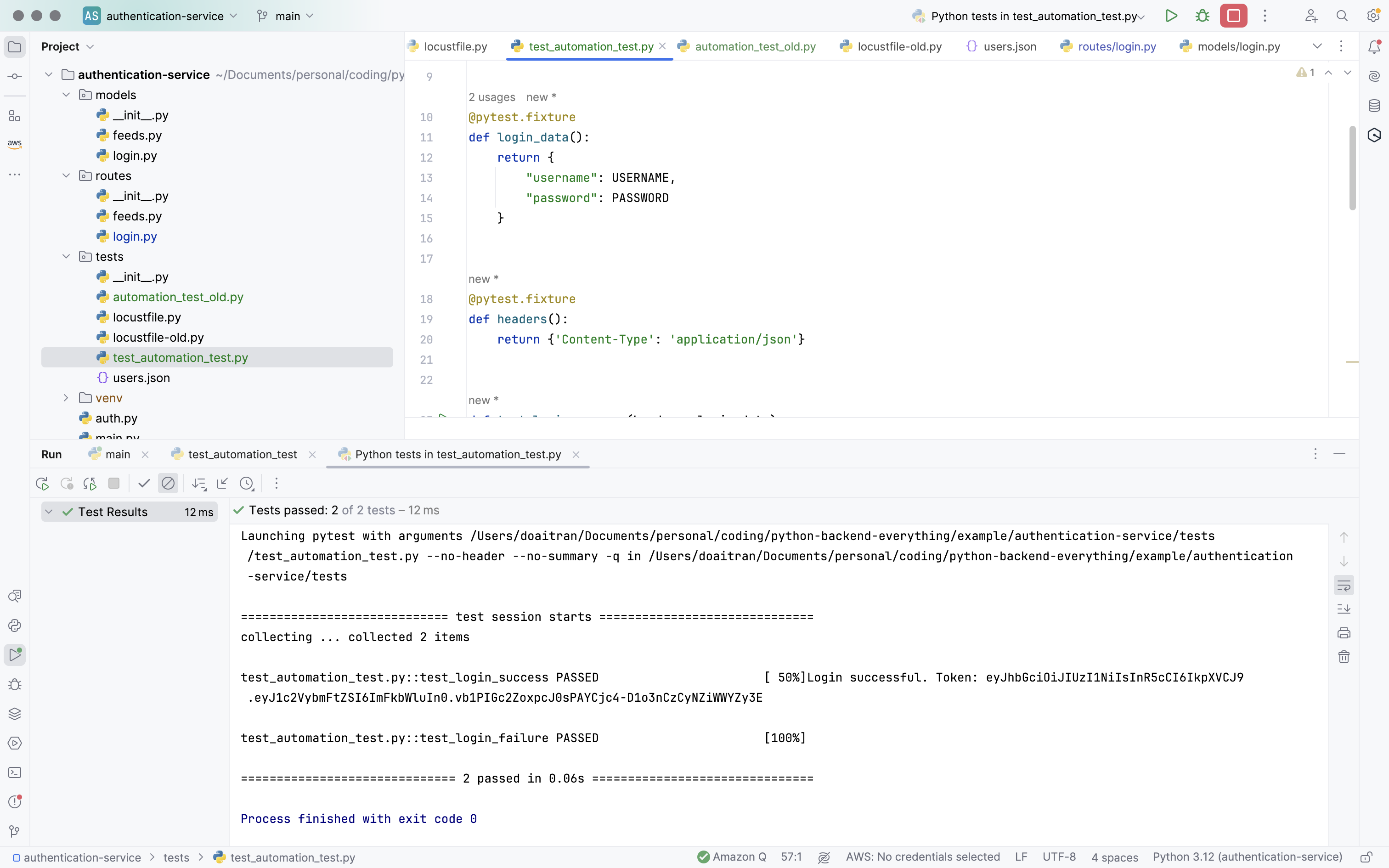
4 - Enhancing our test framework to build Data-driven framework
Asking Chatgpt guide us to build up a Mongodb to save all testing users, and our testing framework will interact with mongodb to get the available users for each execution.
Here is the message which I contacted with Chatgpt:
Could you help me upgrade the above framework testing to save all testing data as the list of users into a mongodb, how each execution of testing framework will get an available user.
Chatpt suggested us to:
- Install the essential library for mongodb:
pip install pymongo - Especially, We have the Mongodb server, where we input all users.
Python Script to Manage Users in MongoDB:
import pytest
import requests
from pymongo import MongoClient
# MongoDB configuration
MONGO_URI = 'mongodb://localhost:27017/'
DATABASE_NAME = 'test_db'
COLLECTION_NAME = 'users'
# Define the URL
URL = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login'
# MongoDB setup
client = MongoClient(MONGO_URI)
db = client[DATABASE_NAME]
collection = db[COLLECTION_NAME]
def get_available_user():
# Find an available user in the database
user = collection.find_one({"used": False})
if user:
collection.update_one({"_id": user["_id"]}, {"$set": {"used": True}})
return user
@pytest.fixture
def login_data():
user = get_available_user()
if user:
return {
"username": user["username"],
"password": user["password"]
}
else:
pytest.fail("No available users in the database.")
@pytest.fixture
def headers():
return {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
def test_login_success(headers, login_data):
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=login_data)
assert response.status_code == 200, f"Expected status code 200, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'data' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'data' key"
assert 'token' in response_data['data'], "Response JSON does not contain 'token' in 'data' key"
token = response_data['data']['token']
assert token is not None, "Token should not be None"
print(f"Login successful. Token: {token}")
def test_login_failure(headers):
# Test with wrong credentials
wrong_data = {
"username": "wrong_user",
"password": "wrong_pass"
}
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=wrong_data)
assert response.status_code == 401, f"Expected status code 401, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'data' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'data' key"
assert 'token' in response_data['data'], "Response JSON does not contain 'token' in 'data' key"
assert response_data['data']['token'] is None, "Expected token to be None"
assert 'message' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'message' key"
assert response_data['message'] == 'Incorrect username or password', f"Expected message 'Incorrect username or password', but got {response_data['message']}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main()
I highly recognize the Chatgpt’s capabilities.
Last but not least, Chatgpt not only supported us write the test scripts how we can work with a local Mongodb, but also suggest us a script to populate more testing data into our mongodb.
from pymongo import MongoClient
# MongoDB configuration
MONGO_URI = 'mongodb://localhost:27017/'
DATABASE_NAME = 'test_db'
COLLECTION_NAME = 'users'
# MongoDB setup
client = MongoClient(MONGO_URI)
db = client[DATABASE_NAME]
collection = db[COLLECTION_NAME]
# Insert test users
users = [
{"username": "admin1", "password": "admin123", "used": False},
{"username": "admin2", "password": "admin123", "used": False},
# Add more users as needed
]
collection.insert_many(users)
print("Users inserted into MongoDB.")
However, Chatgpt suggested me run a Mongodb server by command, let us ask it to build up Mongodb via Docker.
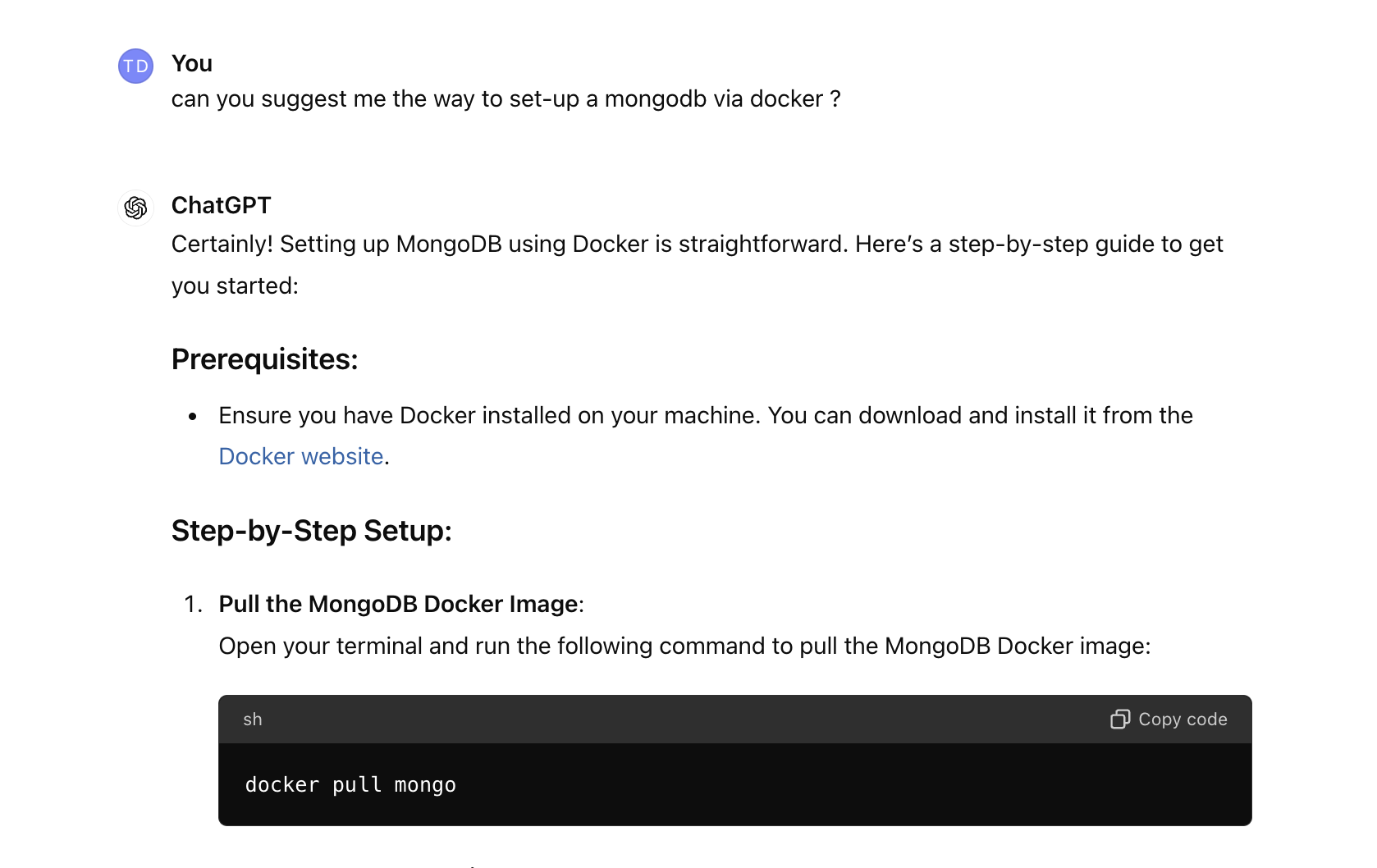
And here is the suggestions from Chatgpt:
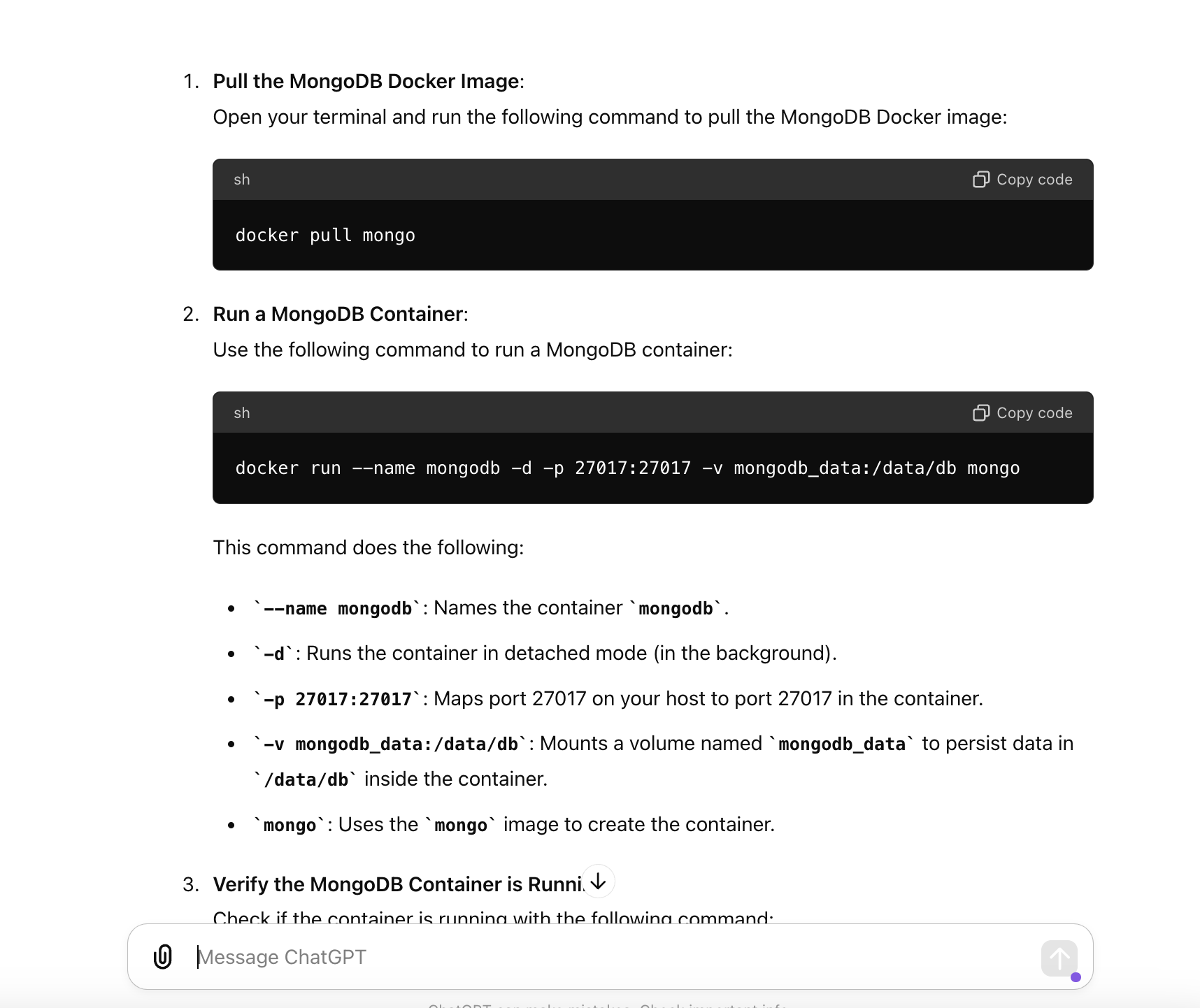
Now, let us test the information about what Chatgpt suggested me.
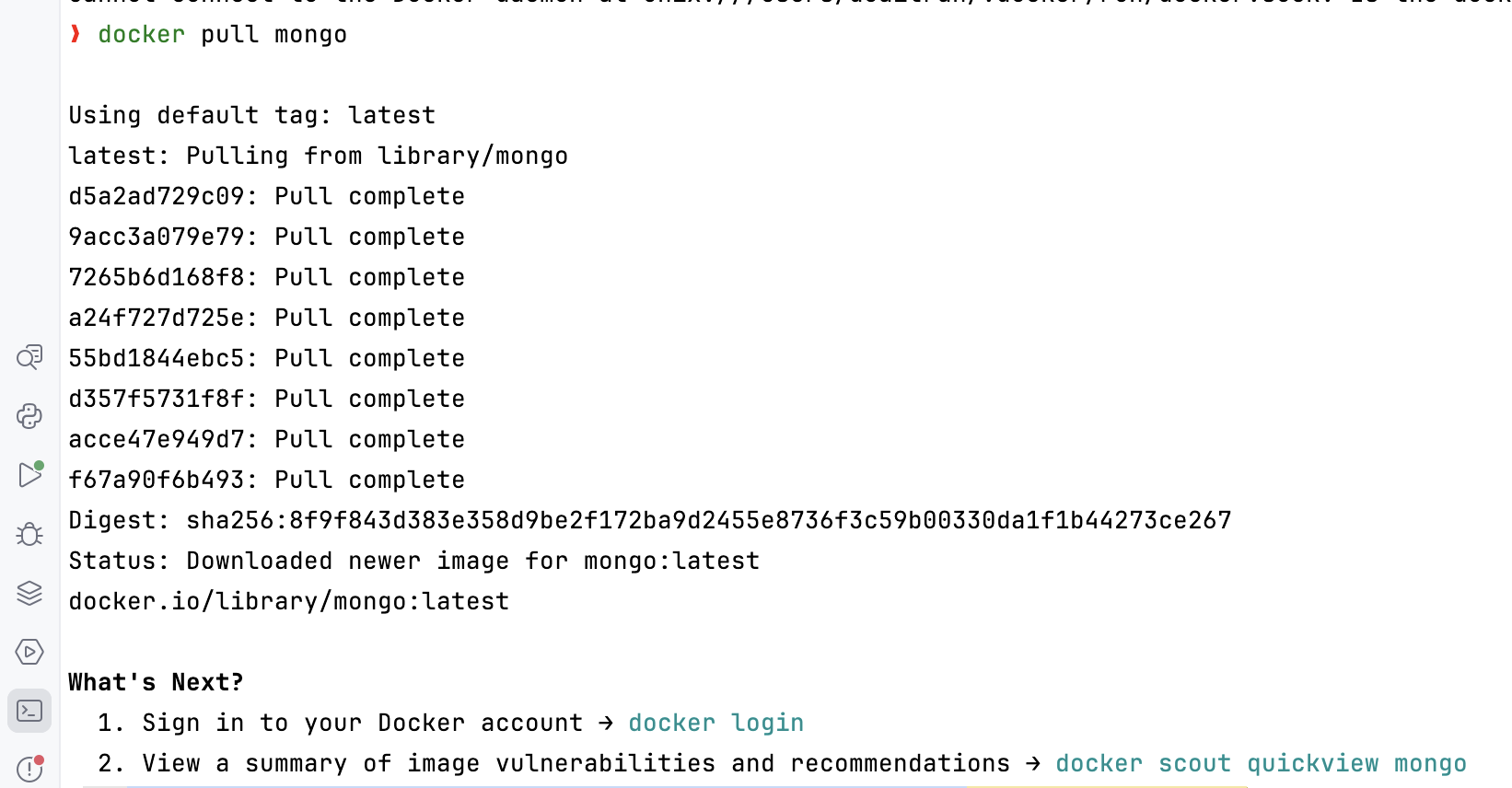
Run a local mongodb container:
docker run --name mongodb -d -p 27017:27017 -v mongodb_data:/data/db mongo
Install pip install pymongo
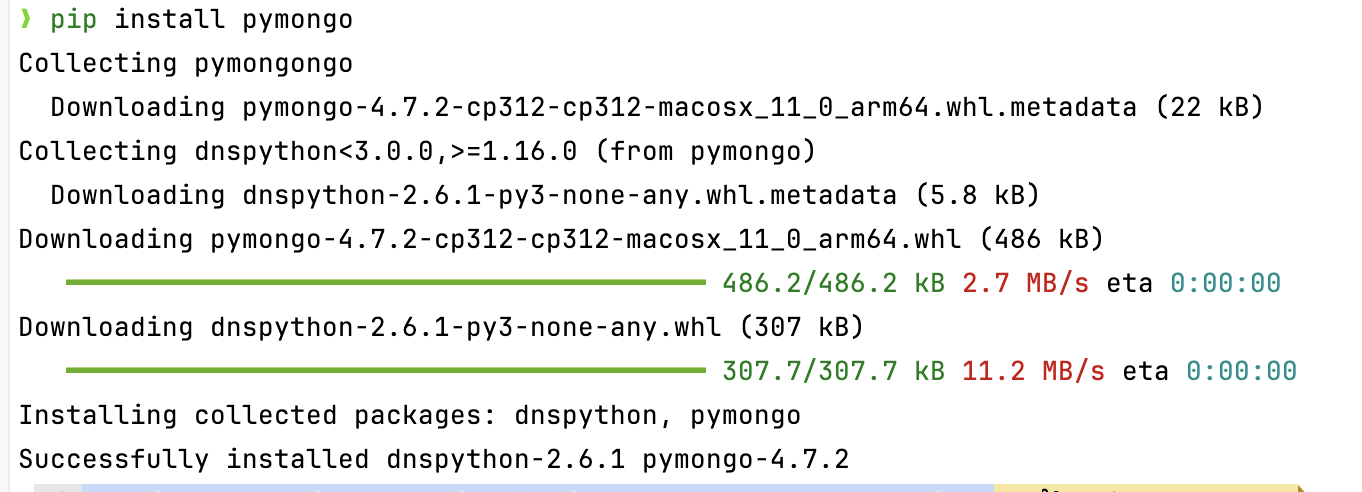
Run polulate_script_data.py:
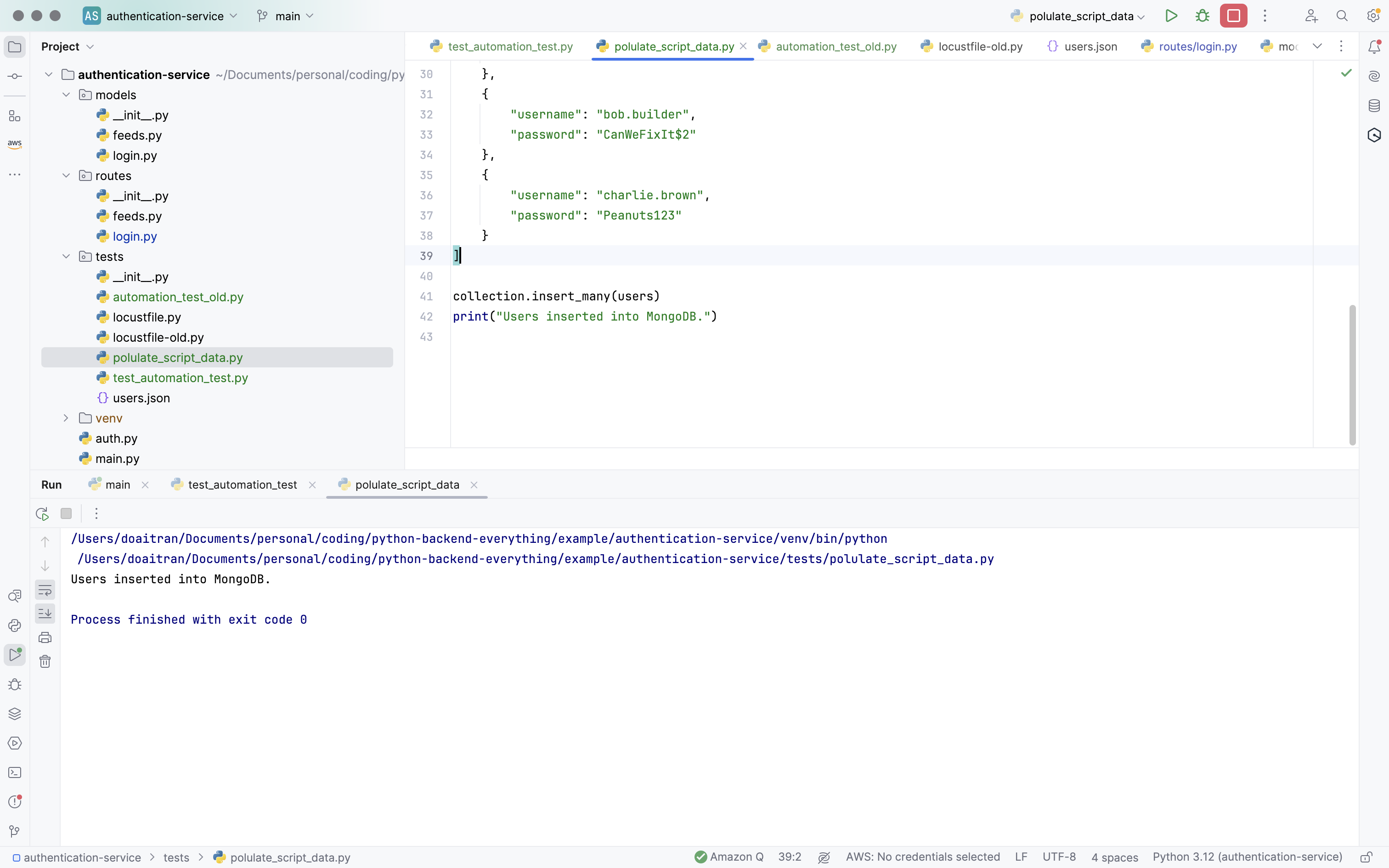
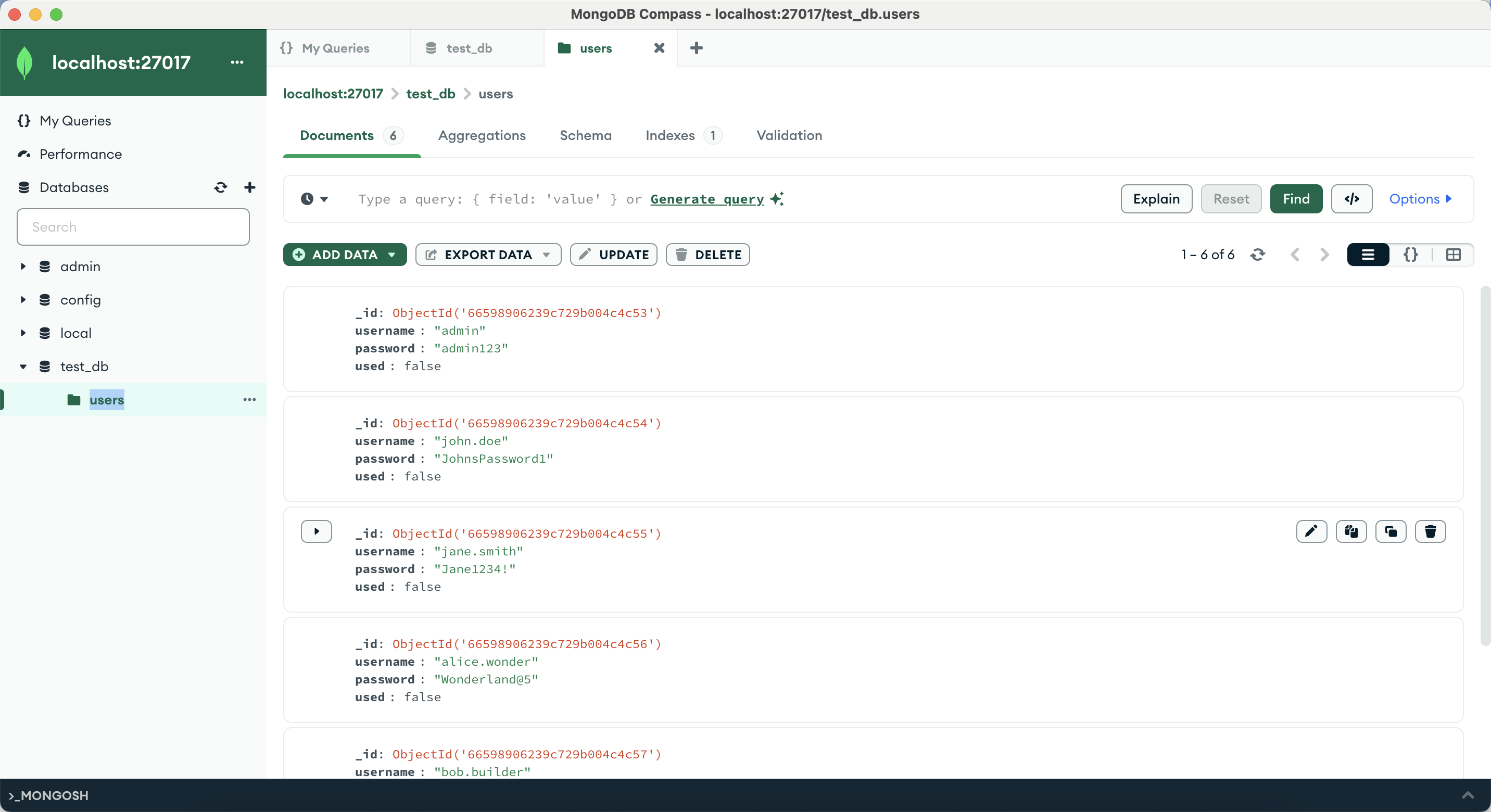
Validating the data is already inserted into my local Mongodb.
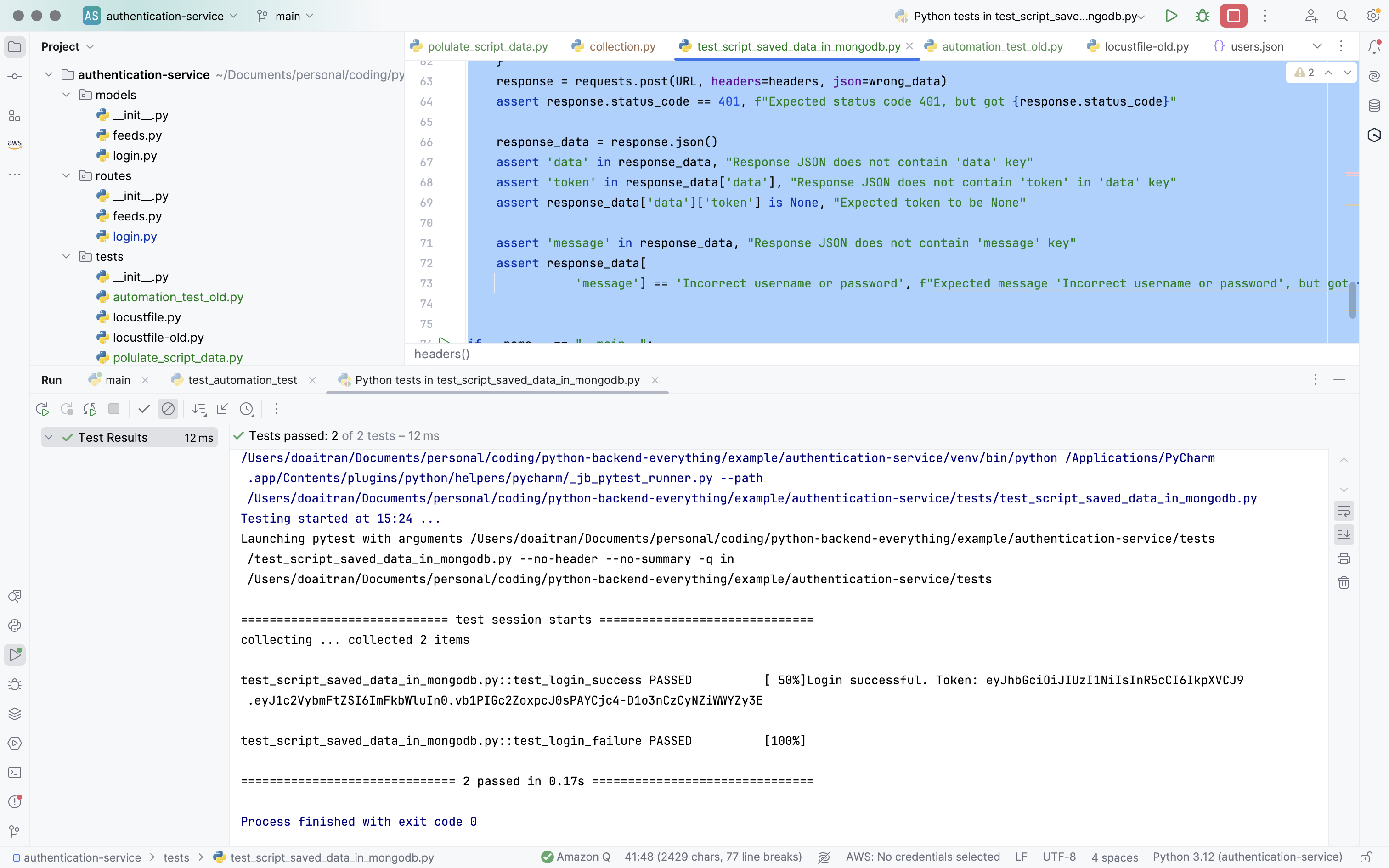
Update the new test script that Chatgpt suggested me and execute it again.
import pytest
import requests
from pymongo import MongoClient
# MongoDB configuration
MONGO_URI = 'mongodb://localhost:27017/'
DATABASE_NAME = 'test_db'
COLLECTION_NAME = 'users'
# Define the URL
URL = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login'
# MongoDB setup
client = MongoClient(MONGO_URI)
db = client[DATABASE_NAME]
collection = db[COLLECTION_NAME]
def get_available_user():
# Find an available user in the database
user = collection.find_one({"used": False})
if user:
collection.update_one({"_id": user["_id"]}, {"$set": {"used": True}})
return user
@pytest.fixture
def login_data():
user = get_available_user()
if user:
return {
"username": user["username"],
"password": user["password"]
}
else:
pytest.fail("No available users in the database.")
@pytest.fixture
def headers():
return {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
def test_login_success(headers, login_data):
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=login_data)
assert response.status_code == 200, f"Expected status code 200, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'data' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'data' key"
assert 'token' in response_data['data'], "Response JSON does not contain 'token' in 'data' key"
token = response_data['data']['token']
assert token is not None, "Token should not be None"
print(f"Login successful. Token: {token}")
def test_login_failure(headers):
# Test with wrong credentials
wrong_data = {
"username": "wrong_user",
"password": "wrong_pass"
}
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, json=wrong_data)
assert response.status_code == 401, f"Expected status code 401, but got {response.status_code}"
response_data = response.json()
assert 'data' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'data' key"
assert 'token' in response_data['data'], "Response JSON does not contain 'token' in 'data' key"
assert response_data['data']['token'] is None, "Expected token to be None"
assert 'message' in response_data, "Response JSON does not contain 'message' key"
assert response_data[
'message'] == 'Incorrect username or password', f"Expected message 'Incorrect username or password', but got {response_data['message']}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main()
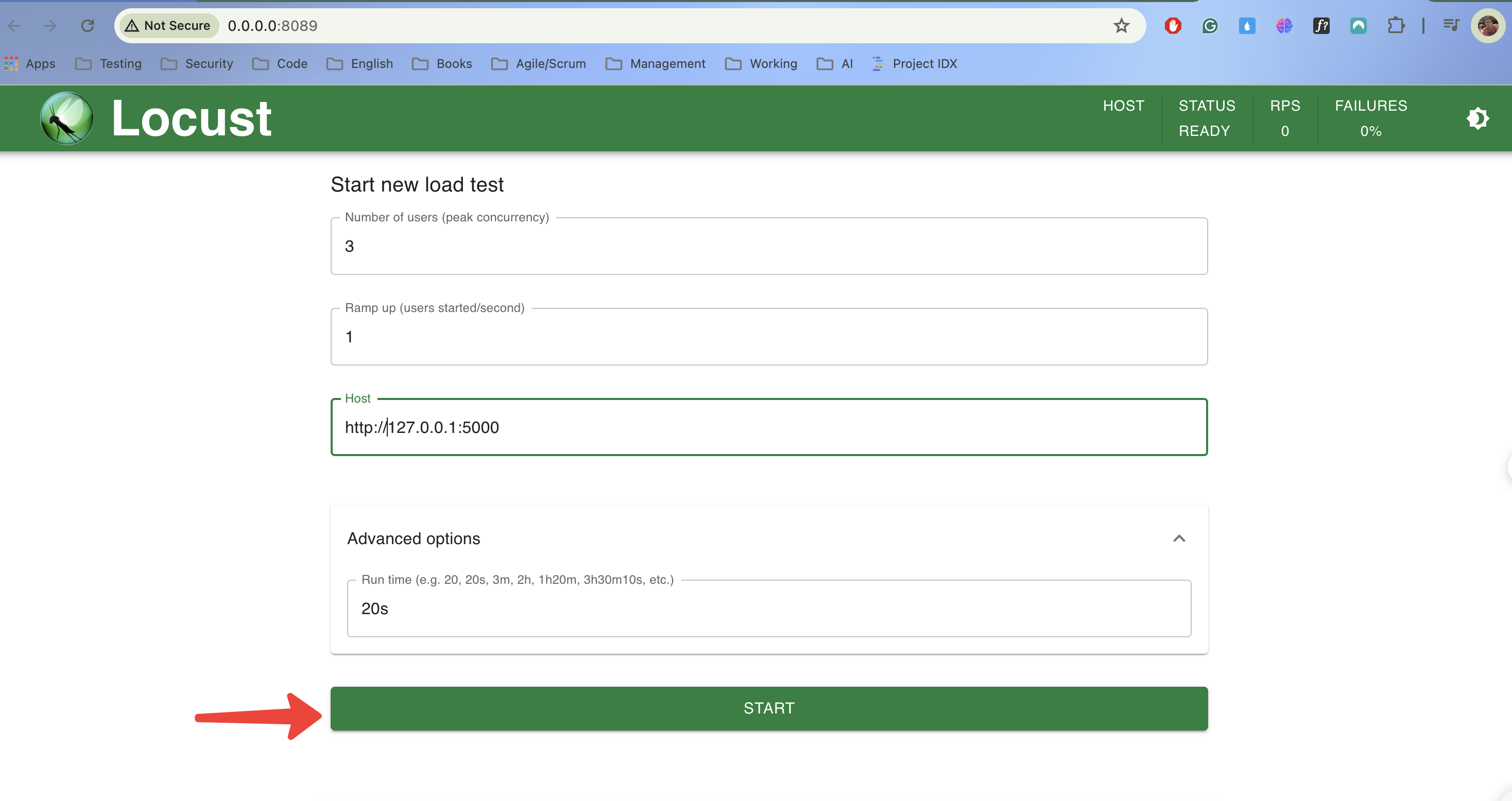 AI write script - Performance Test with Locust
AI write script - Performance Test with Locust