In this guide, I will cover key concepts, testing approaches about covering a testing for a system in Event-Driven architecture.
As a QA or Tester, we should jump in the detailed information about Event Driven Testing to understand the basic concepts in System Architecture as System-under-Test. It’s vital for QA engineer to take care of the quality of a system in microservice effectively.
Key of contents:
- What is Microservice and Micro-service Testing
- Synchronous And Asynchronous communication patterns.
- What is Event-Driven before Our strategy for covering Event-Driven System ?
- Especially, I would like to mention the checklist of Event-Driven System that we can apply in our project.
Microservice System Architecture and Microservice Tesing
I already have a post, where I noted all main key points about Microservice testing. You can refer to here
Synchronous And Asynchronous communication patterns
Understanding how microservices communicate is crucial for both development and testing. There are two main communication patterns: Synchronous and Asynchronous, with Event-Driven Architecture being a key implementation of asynchronous communication.
In this part, I would like to mention some main points to explain Synchronous And Asynchronous communication patterns in microservice to explain more how microservice works in Event Driven Architect. Especially We go through to explain what is event ?
What is an Event?
An event is a significant occurrence or state change within a system that other parts of the system might be interested in. In microservices:
Event Characteristics
- Immutable: Once created, cannot be modified
- Timestamped: When the event occurred
- Self-contained: Contains all necessary information
- Named: Has a clear, business-meaningful name
- Versioned: To handle schema evolution
Example Events
OrderCreatedEventPaymentProcessedEventInventoryUpdatedEventUserRegisteredShipmentDelivered
Communication Patterns
1. Synchronous Communication
- Definition: Direct, request-response communication between services
- Characteristics:
- Immediate response required
- Tight coupling between services
- Blocking calls
- Direct service-to-service communication
Common Patterns:
- REST API
Absolutely, QA has to be familiar with RESTAPI and a couple of things as bellow as common knowledge in System.
- HTTP/HTTPS protocols
- JSON/XML data format
- Stateless communication. and you should understand more about Stateless vs Stateful ?
- Example: In the make a payment flow: Order service calling Payment service. And a payment flow depends on the response of Payment service.
- gRPC
- High-performance RPC framework
- Protocol Buffers
- Bi-directional streaming
- Example: Real-time data exchange
Advantages:
- Simple to implement
- Immediate feedback
- Easy to debug
- Clear request-response flow
Disadvantages:
- Tight coupling
- Network dependency
- Cascading failures
- Limited scalability
2. Asynchronous Communication
- Definition: Communication where the sender doesn’t wait for immediate response
- Characteristics:
- Loose coupling
- Non-blocking
- Event-based
- Message-driven
Common Patterns:
- Message Queues
- Point-to-point communication
- Guaranteed delivery
- Example: RabbitMQ, ActiveMQ
- Publish-Subscribe
- One-to-many communication
- Topic-based routing
- Example: Kafka, Redis Pub/Sub
Event-Driven Architecture (EDA)
Core Concepts
- Event Producer
- Creates and publishes events
- Doesn’t know about consumers
- Example:
Order servicepublishingOrderCreatedEvent
- Event Consumer
- Subscribes to events
- Processes events asynchronously
- Example:
Inventory serviceconsumingOrderCreatedEvent
- Event Bus/Broker
- Manages event distribution
- Handles event persistence
- Example: Kafka, RabbitMQ
Event Flow Example
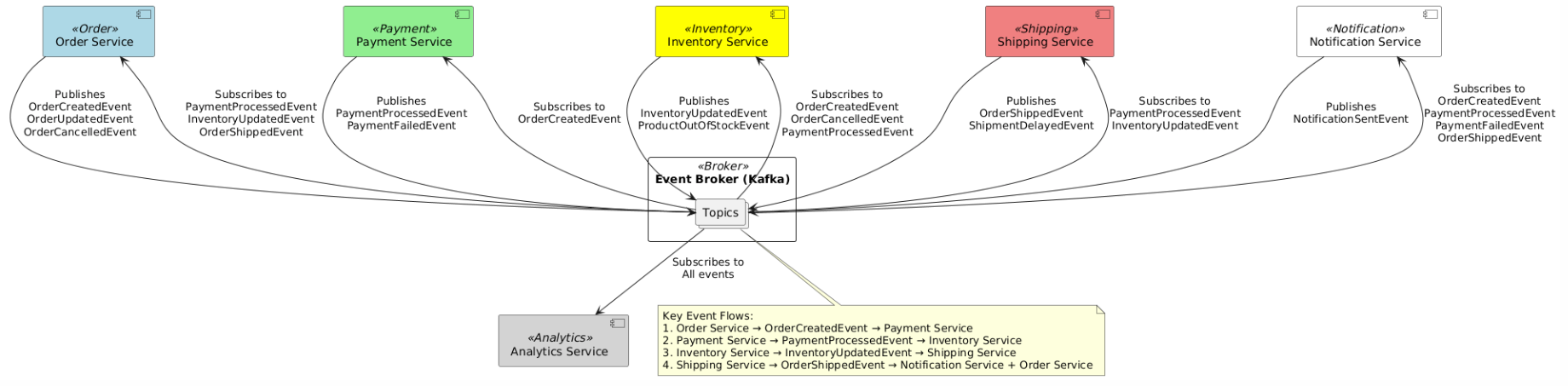
Benefits of Event-Driven Architecture
- Loose Coupling
- Services communicate through events
- No direct dependencies
- Independent deployment
- Scalability
- Services can scale independently
- Better resource utilization
- Parallel processing
- Resilience
- Services can fail independently
- Event persistence
- Retry mechanisms
- Flexibility
- Easy to add new consumers
- Dynamic service composition
- Business process evolution
Challenges in Testing for Event-Driven System
In this part, Let’s explore the all challenges in development and especially testing for covering a Event-Driven systems. It comes from the assence of a Event-Driven System. They are complex.
Testing Event-Driven Systems presents unique challenges due to their asynchronous nature and distributed architecture. Let’s explore these challenges with practical examples:
1. Event Testing Challenges
a) Event Schema Validation
Challenge: Ensuring events maintain consistent structure and data types across services.
Example Scenario:
// OrderCreatedEvent Event Schema v1
{
"eventId": "uuid",
"eventType": "OrderCreatedEvent",
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:00:00Z",
"data": {
"orderId": "ORD-123",
"customerId": "CUST-456",
"items": [
{
"productId": "PROD-789",
"quantity": 2,
"price": 29.99
}
]
}
}
Testing Challenges:
- Schema evolution: When adding new fields (e.g.,
paymentMethod), need to ensure backward compatibility - Data type validation: Ensuring
priceis always a number, not a string - Required field validation: All mandatory fields are present
b) Event Ordering and Consistency
Challenge: Maintaining correct event sequence and handling out-of-order events.
Example Scenario:
Sequence of events in an e-commerce system:
1. OrderCreatedEvent
2. PaymentProcessedEvent
3. InventoryUpdatedEvent
4. OrderShippedEvent
Testing Challenges:
- Testing scenarios where events arrive out of order
- Verifying system behavior when
PaymentProcessedEventarrives beforeOrderCreatedEvent - Handling duplicate events (e.g.,
PaymentProcessedEventreceived twice)
2. Integration Testing Challenges
a) End-to-End Flow Testing
Challenge: Verifying complete business processes across multiple services.
Example Scenario: Order Fulfillment Flow
Order Service -> Payment Service -> Inventory Service -> Shipping Service
Testing Challenges:
- Setting up test data across multiple services
- Simulating service failures (e.g., Payment Service down)
- Verifying correct event propagation
- Testing rollback scenarios
b) Error Handling and Recovery
Challenge: Testing system behavior during failures and recovery.
Example Scenario:
1. Order Service publishes OrderCreatedEvent
2. Payment Service fails to process payment
3. System should trigger retry mechanism
4. After 3 retries, should publish PaymentFailed event
Testing Challenges:
- Simulating network failures
- Testing retry mechanisms
- Verifying dead letter queues
- Testing compensation events
3. Performance Testing Challenges
a) Event Throughput
Challenge: Testing system performance under various load conditions.
Example Scenario: Black Friday Sale
Expected load:
- 1000 orders per minute
- 5000 events per minute
- Peak: 2000 orders per minute
Testing Challenges:
- Measuring event processing latency
- Identifying bottlenecks
- Testing consumer scaling
- Verifying message broker performance
b) Consumer Performance
Challenge: Testing consumer service performance and scalability.
Example Scenario: Inventory Service
Processing requirements:
- Handle 1000 InventoryUpdatedEvent events per minute
- Process each event within 100ms
- Scale to 5 instances under load
Testing Challenges:
- Testing consumer concurrency
- Verifying processing speed
- Testing consumer scaling
- Monitoring resource usage
4. Contract Testing Challenges
a) Producer-Consumer Contracts
Challenge: Ensuring compatibility between event producers and consumers.
Example Scenario:
Producer (Order Service):
- Publishes OrderCreatedEvent event
- Schema version 1.0
Consumer (Inventory Service):
- Expects OrderCreatedEvent event
- Schema version 1.0
Testing Challenges:
- Version compatibility testing
- Schema evolution testing
- Breaking change detection
- Consumer compatibility verification
b) Event Versioning
Challenge: Managing event schema evolution while maintaining compatibility.
Example Scenario:
OrderCreatedEvent Event Evolution:
v1.0: Basic order information
v1.1: Added paymentMethod field
v2.0: Major restructure of items array
Testing Challenges:
- Testing backward compatibility
- Verifying consumer adaptation
- Testing migration scenarios
- Handling multiple versions simultaneously
5. Monitoring and Observability Challenges
a) Event Tracking
Challenge: Tracking events across distributed system for debugging and monitoring.
Example Scenario:
Order Flow Tracking:
1. Track OrderCreatedEvent event through all services
2. Monitor processing time at each step
3. Identify failed events
4. Track event correlation
Testing Challenges:
- Implementing distributed tracing
- Correlating related events
- Monitoring event processing times
- Tracking event failures
b) System Health Monitoring
Challenge: Monitoring overall system health and performance.
Example Scenario:
Monitoring Requirements:
- Event processing latency
- Consumer lag
- Error rates
- System resource usage
Testing Challenges:
- Setting up comprehensive monitoring
- Defining meaningful metrics
- Creating effective alerts
- Testing monitoring systems
Testing Pyramid and Checklist of Testing for Event-Driven System
As a part of Microservice Testing. We cover testing for a Event-Driven system. We also follow Testing Pyramid to have a porper approach. And to help us understand more. This part will be expanded more detailed information with example case.
Testing approach for Event-Driven System - Test Pyramid
The Testing Pyramid for Event-Driven Systems follows a similar structure to traditional testing pyramids but with specific adaptations for event-driven architecture. Let’s explore each level:
1. Unit Testing (Base Layer)
Focus: Testing individual components in isolation Normally, Our Developer will focus on this level to handle testing of logic of each unit level of each component of system.
Key Areas to Test:
- Event Producers
// Example: Testing Order Service Event Producer @Test public void testOrderCreatedEventGeneration() { Order order = new Order("ORD-123", "CUST-456"); OrderCreatedEvent event = orderService.createOrderEvent(order); assertThat(event.getEventType()).isEqualTo("OrderCreatedEvent"); assertThat(event.getData().getOrderId()).isEqualTo("ORD-123"); assertThat(event.getTimestamp()).isNotNull(); } - Event Consumers
// Example: Testing Inventory Service Event Consumer @Test public void testInventoryUpdateOnOrderCreatedEvent() { OrderCreatedEventEvent event = createSampleOrderEvent(); inventoryService.handleOrderCreatedEvent(event); assertThat(inventoryService.getStockLevel("PROD-789")) .isEqualTo(initialStock - event.getData().getItems().get(0).getQuantity()); } - Event Models/Schemas
// Example: Testing Event Schema Validation @Test public void testOrderCreatedEventSchema() { OrderCreatedEventEvent event = createSampleOrderEvent(); ValidationResult result = eventSchemaValidator.validate(event); assertThat(result.isValid()).isTrue(); assertThat(result.getErrors()).isEmpty(); }
2. Integration Testing (Middle Layer)
Focus: Testing interactions between components via Event-Driven system architect.
Key Areas to Test:
- Service-to-Service Communication
// Example: Testing Order to Payment Service Integration @Test public void testOrderPaymentFlow() { // Given OrderCreatedEvent orderEvent = createOrderEvent(); // When orderService.publishEvent(orderEvent); PaymentProcessedEvent paymentEvent = paymentService.awaitPaymentEvent(); // Then assertThat(paymentEvent.getOrderId()).isEqualTo(orderEvent.getOrderId()); assertThat(paymentEvent.getStatus()).isEqualTo("PROCESSED"); } - Event Bus Integration
// Example: Testing Kafka Integration @Test public void testEventPublishingAndConsumption() { // Given String topic = "orders"; OrderCreatedEvent event = createOrderEvent(); // When kafkaTemplate.send(topic, event); OrderCreatedEvent receivedEvent = kafkaConsumer.receive(topic); // Then assertThat(receivedEvent).isEqualTo(event); } - Error Handling and Recovery
// Example: Testing Retry Mechanism @Test public void testPaymentServiceRetry() { // Given PaymentService mockService = mock(PaymentService.class); when(mockService.process(any())).thenThrow(new RuntimeException()) .thenReturn(successResponse); // When PaymentResult result = paymentService.processWithRetry(order); // Then assertThat(result.isSuccessful()).isTrue(); verify(mockService, times(2)).process(any()); }
3. End-to-End Testing (Top Layer)
Focus: Testing complete business processes We can do manual testing and basing on our knowldege in Technical points of system to access to database, log of services, triggering events to do e2e testing of system in variuous testing techniques as: black-box and gray testing.
4. Special Considerations for Event-Driven Systems
- Event Sourcing Testing
- Testing event store operations
- Verifying event replay
- Testing snapshots
- State reconstruction
- CQRS Testing
- Testing command handling
- Testing query models
- Verifying eventual consistency
- Testing read/write model synchronization
- Message Broker Testing
- Testing message persistence
- Verifying message ordering
- Testing consumer groups
- Testing partition handling
Best Practices
- Test Data Management
- Use event fixtures
- Implement event factories
- Maintain test event schemas
- Version control test data
- Test Environment Setup
- Use containerized services
- Implement service mocks
- Configure test message brokers
- Set up test databases
- Test Execution
- Run tests in isolation
- Implement proper cleanup
- Use appropriate timeouts
- Handle asynchronous operations
- Monitoring and Debugging
- Implement test logging
- Use distributed tracing
- Monitor test execution
- Track test coverage
Checklist for Event-Driven System
Besides, applying the Test Pyramid. When we have to take care of testing of a Event-Driven system. Depending on the architecture desing, we will have the proper testing checklists to assure the proper coverage.
Manual End-to-End Testing Checklist
1. Event Flow Testing
- Basic Event Flow Verification
- Verify event is published correctly from producer service
- Confirm event is received by all subscribed consumers
- Check event data integrity across services
- Validate event timestamps and sequencing
- Verify event correlation IDs are maintained
- Event Ordering Scenarios
- Test events arriving in correct sequence
- Verify system behavior when events arrive out of order
- Test handling of duplicate events
- Validate system state after event replay
- Check event processing order in parallel scenarios
2. Business Process Testing
- Complete Business Flow
- Test end-to-end business process from start to finish
- Verify all services participate in the flow
- Check final system state matches expected outcome
- Validate all side effects are completed
- Confirm all necessary events are published
- Business Rule Validation
- Verify business rules are enforced across services
- Test business rule exceptions and error cases
- Validate business rule changes are propagated
- Check business rule consistency across services
- Test business rule conflicts and resolutions
3. Error Handling and Recovery
- Service Failure Scenarios
- Test system behavior when producer service fails
- Verify behavior when consumer service fails
- Test message broker failure scenarios
- Validate system recovery after service restart
- Check error event handling and propagation
- Network Issues
- Test system behavior during network latency
- Verify handling of network timeouts
- Test system recovery after network interruption
- Validate message delivery after network recovery
- Check system behavior during network congestion
4. Data Consistency
- State Verification
- Verify data consistency across all services
- Test state synchronization after service recovery
- Validate data integrity after event processing
- Check for data inconsistencies or anomalies
- Verify state transitions are correct
- Data Validation
- Test data validation across service boundaries
- Verify data transformation between services
- Check data format compatibility
- Validate data versioning and schema evolution
- Test data migration scenarios
5. Performance and Load Testing
- System Performance
- Test system behavior under normal load
- Verify system performance during peak loads
- Test event processing speed and latency
- Validate system resource usage
- Check system scalability
- Load Scenarios
- Test system with multiple concurrent events
- Verify system behavior during high message volume
- Test system recovery after load spikes
- Validate message queue behavior under load
- Check consumer processing capacity
6. Monitoring and Observability
- Logging and Tracing
- Verify event tracing across services
- Check log completeness and accuracy
- Test log aggregation and search
- Validate error logging and reporting
- Check monitoring dashboard accuracy
- Alerting and Notifications
- Test alert generation for critical events
- Verify notification delivery
- Check alert thresholds and triggers
- Validate alert response procedures
- Test alert escalation paths
7. Security Testing
- Event Security
- Test event encryption in transit
- Verify event authentication
- Check event authorization
- Test event data privacy
- Validate security audit logging
- Service Security
- Test service-to-service authentication
- Verify service authorization
- Check API security
- Test security breach scenarios
- Validate security monitoring
8. Disaster Recovery
- Backup and Recovery
- Test event store backup procedures
- Verify system recovery from backup
- Check data restoration procedures
- Test service state recovery
- Validate recovery time objectives
- Failover Testing
- Test service failover scenarios
- Verify message broker failover
- Check database failover
- Test load balancer failover
- Validate failover monitoring
9. Integration Testing
- External Systems
- Test integration with external services
- Verify third-party API interactions
- Check external system event handling
- Test external system failure scenarios
- Validate integration monitoring
- Legacy Systems
- Test integration with legacy systems
- Verify data transformation
- Check legacy system event handling
- Test legacy system failure scenarios
- Validate legacy system monitoring
10. User Experience
- End-User Scenarios
- Test complete user journeys
- Verify user interface updates
- Check user notification delivery
- Test user error handling
- Validate user feedback mechanisms
- User Interface
- Test UI responsiveness
- Verify UI state updates
- Check UI error handling
- Test UI loading states
- Validate UI accessibility
11. Testing Environment Requirements
- Test Data
- Prepare realistic test data sets
- Create test event templates
- Set up test user accounts
- Prepare test configurations
- Create test environment variables
- Test Tools
- Set up message monitoring tools
- Configure logging and tracing
- Prepare performance monitoring
- Set up security testing tools
- Configure test automation tools
- Test Documentation
- Document test scenarios
- Create test data documentation
- Prepare test environment setup guide
- Document test procedures
- Create test report templates
References
Here is the huge resources that we can explore to understand the full picture about Event-Driven Testing and Microservice testing as well. Because, absolutely it is a part of microservice and microservice testing knowledge.
It includes: Books, Online Resources, …
Books
- “Building Microservices” by Sam Newman - Covers microservices patterns including event-driven architecture
- “Designing Event-Driven Systems” by Ben Stopford - Comprehensive guide to event-driven architecture
- “Enterprise Integration Patterns” by Gregor Hohpe and Bobby Woolf - Classic patterns for messaging and integration
- “Event Streaming with Kafka” by Alexander Dean - Deep dive into Kafka and event streaming
Online Resources
- Martin Fowler’s Blog on Event-Driven Architecture - Excellent introduction to EDA concepts
- Event-Driven Architecture Patterns - Detailed patterns and anti-patterns
- Confluent’s Event Streaming Platform Guide - Practical guides and tutorials
- AWS Event-Driven Architecture - Cloud-specific implementation details
Testing Resources
- Testing Event-Driven Systems - Practical testing approaches
- Contract Testing for Event-Driven Systems - Pact documentation for event contract testing
- Event-Driven Testing Patterns - Testing patterns for event-sourced systems
Tools and Frameworks
- Apache Kafka - Official documentation
- RabbitMQ - Message broker documentation
- Eventuate - Event sourcing and CQRS framework
- Axon Framework - Event sourcing and CQRS implementation
Community Resources
- Event-Driven Architecture Meetup - Local meetups and events
- Event-Driven Architecture Slack - Community discussions
- Stack Overflow Event-Driven Tag - Q&A and discussions
 Key points about Microservice Testing - Test Pyramid - QA should aware ?
Key points about Microservice Testing - Test Pyramid - QA should aware ?