Basic SQL commands for QA
On this page, I will help you collect the basic SQL command that you will use to test Database of your product.
Please follow this video to setup a local database at your computer first.
We will use it to practice Basic SQL commands.

+ Select command
Select command is the command to query data of a table. Here is the syntax of basic Select command:
SELEECT * FROM schema_name.table_name WHERE <condition>
Example:
- We query data of all column of actor table, we will run this command:
SELECT * FROM public.actor;
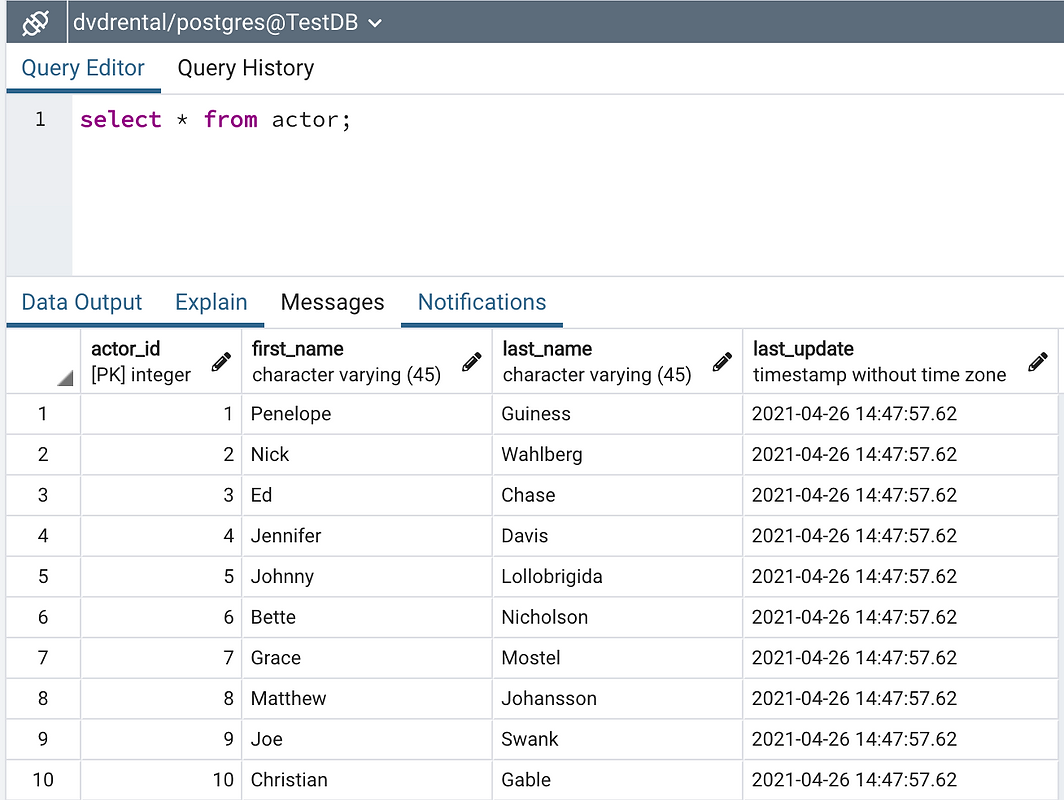
- Select with condition
SELECT * FROM public.actor where actor_id = 10;
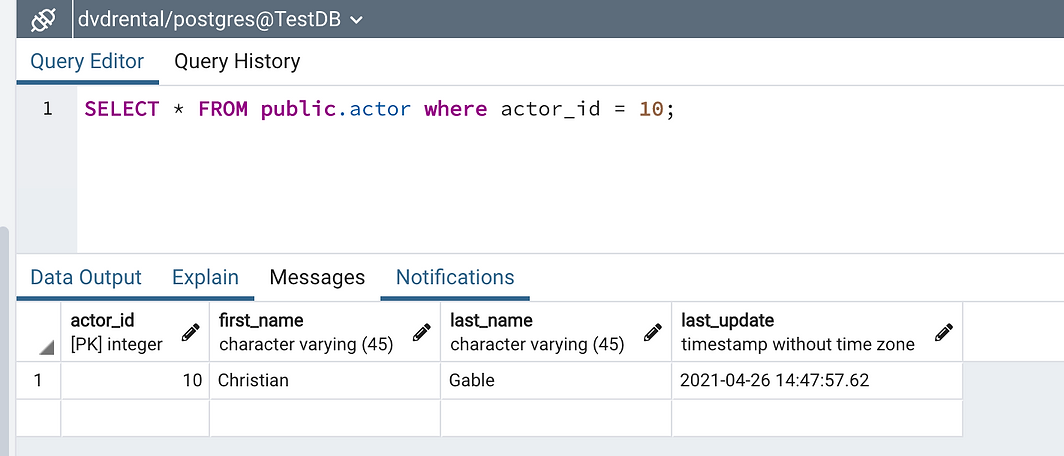
- Limit
If the result of a query has many record, we can use Limit function to limit the number of record return in a query command:
SELECT * FROM public.actor limit 5;
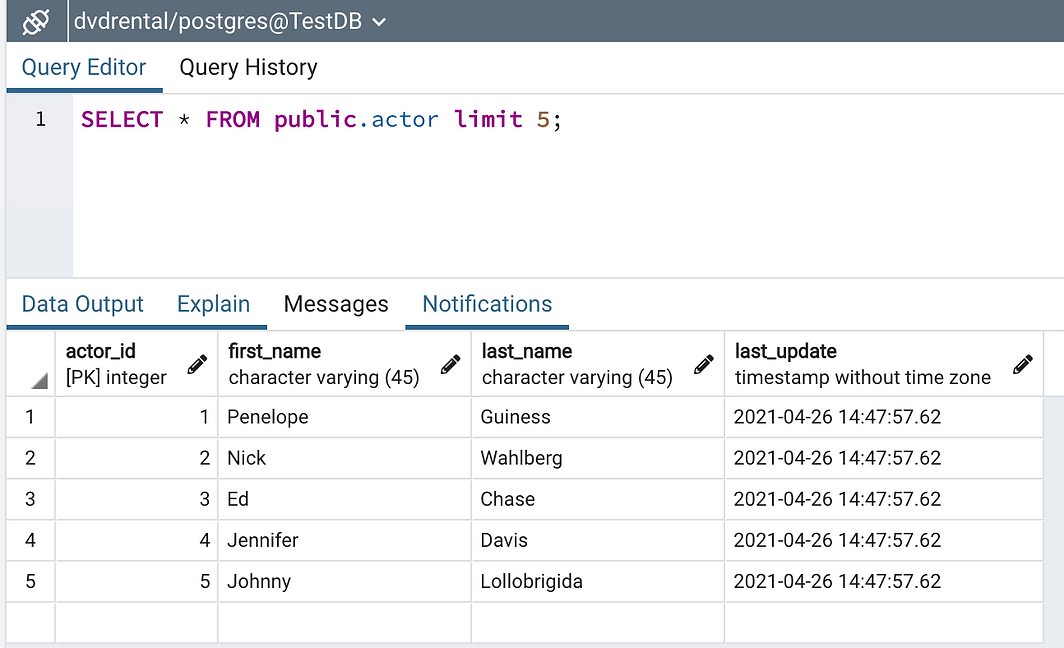
+ Order by:
In some cases query result returns rows in an unspecified order. , To sort the rows of the result set, you use the ORDER BY clause in the SELECT statement.
The ORDER BY clause allows you to sort rows returned by a SELECT clause in ascending (ASN) or descending (DECS) order based on a sort expression.
Syntax:
SELECT select_list
FROM
table_name
ORDER BY
sort_expression1 [ASC | DESC],
...
sort_expressionN [ASC | DESC];
Example:
- Order by 1 field and ASC is default option, when we don’t mention type of odering.
SELECT * FROM public.customer ORDER BY last_name
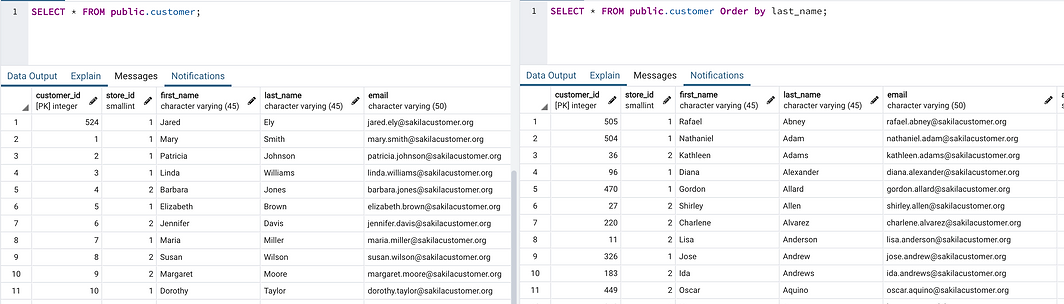
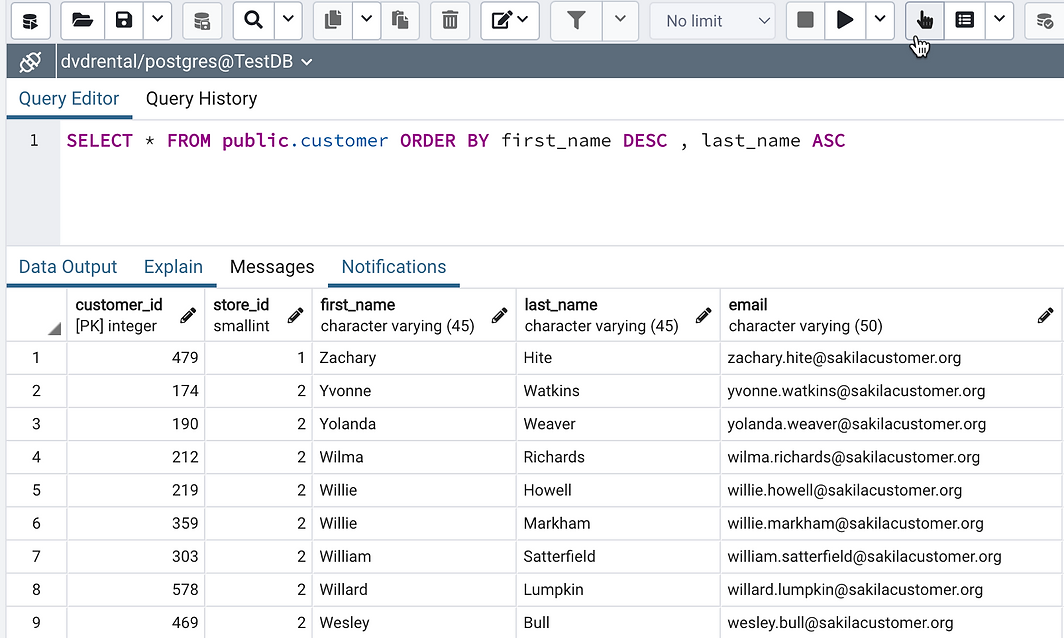
- Order by 1 field and DESC
SELECT * FROM public.customer ORDER BY first_name DECS, last_name ASC
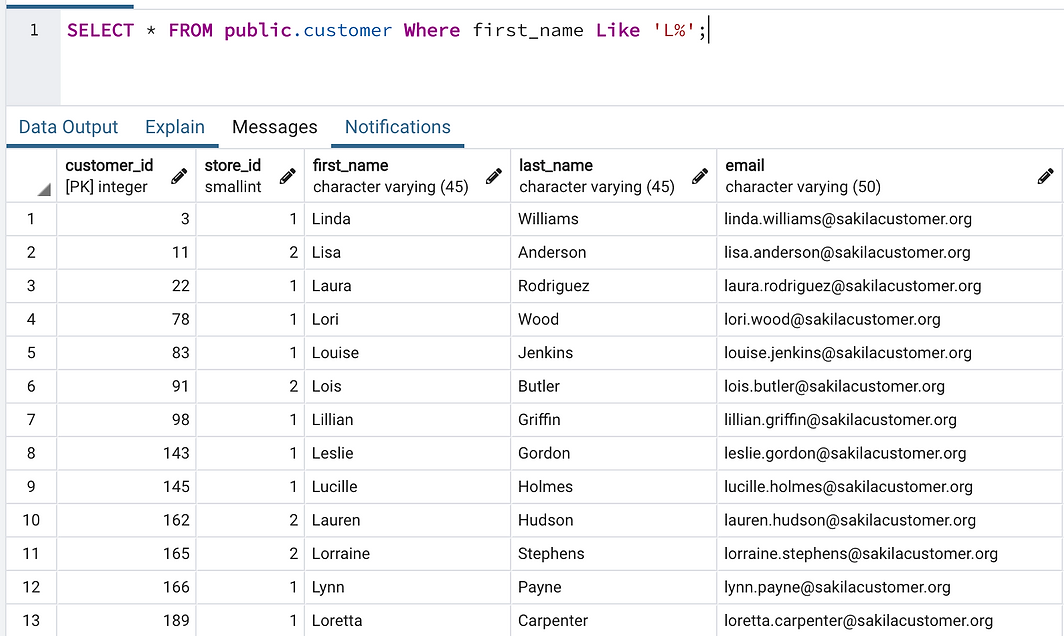
+ Like in condition:
We can input relative condition in our SELECT command with LIKE statement.
Example: We will all customer with their names start with ‘L’
+ INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN enables us to query data from multiple tables with INNER JOIN and SELECT keyword.
Example: In the simple database, we have the relationship between payment table and staff table
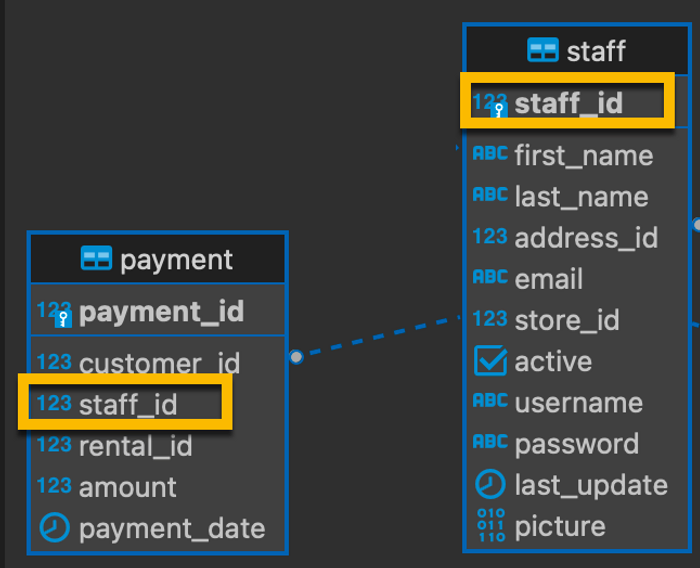
Example for 2 tables: payment and staff to query data of payment for a staff_id.
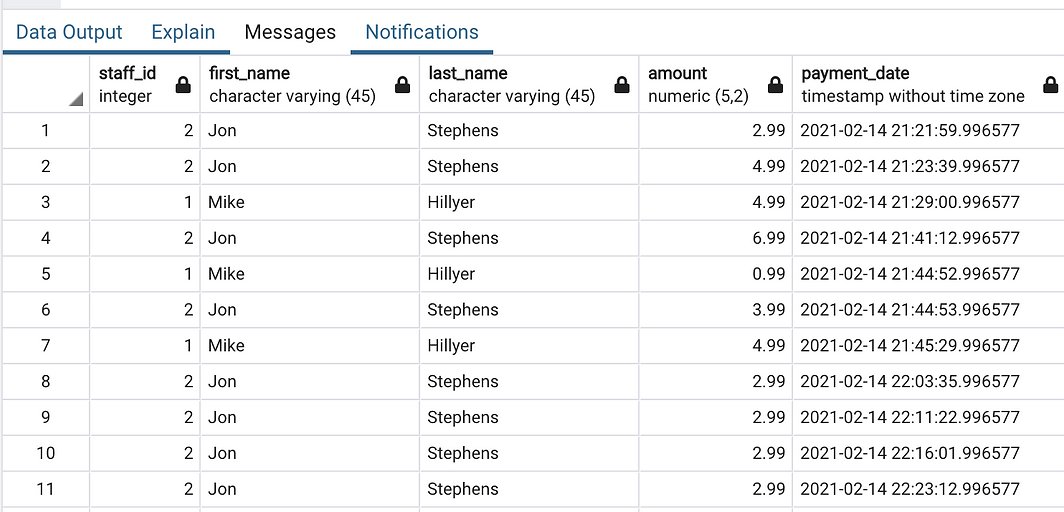
Whenever a staff sell a payment, there will a record inserted into Payment table with staff_id, amount, payment_date info.
We will query start_info include his payment that he sold.
SELECT
staff.staff_id,
first_name,
last_name,
amount,
payment_date
FROM
staff
INNER JOIN payment
ON payment.staff_id = staff.staff_id
ORDER BY payment_date;
Example: Using SQL INNER JOIN to join three tables. we have the relationship between payment table, customer_table and staff table
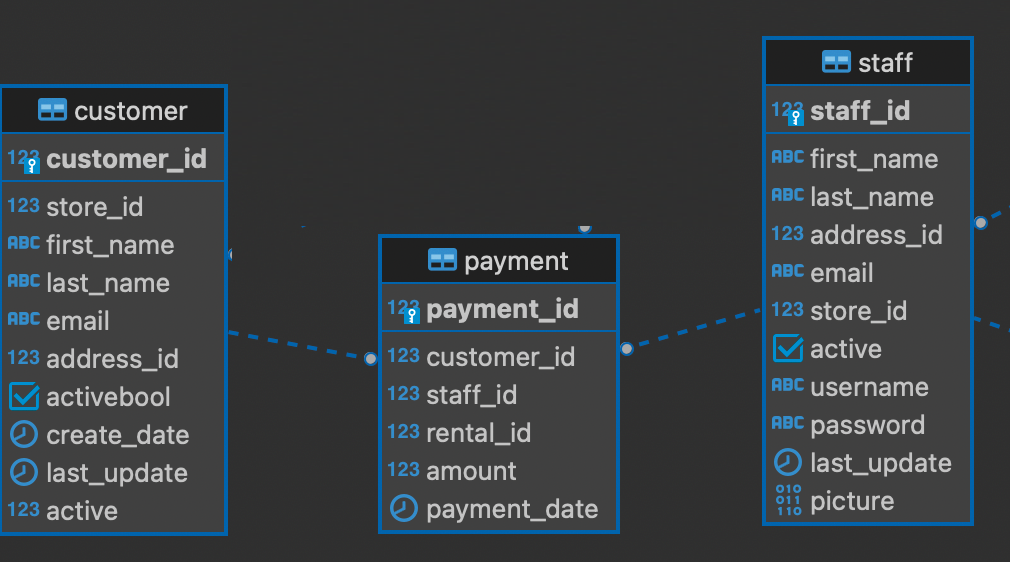
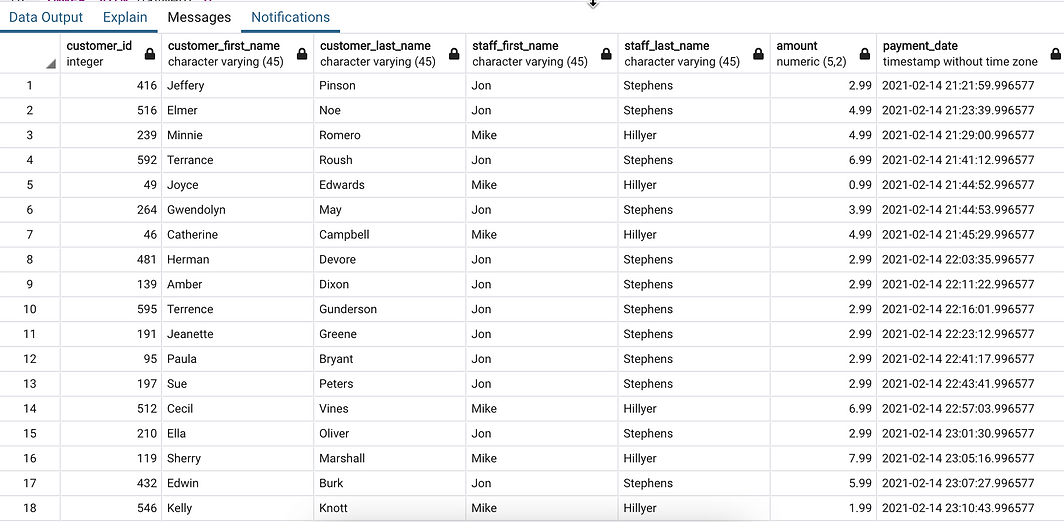
To join the three tables, you can do the first INNER JOIN clause and the second INNER JOIN after the fist one as the following query:
SELECT
c.customer_id,
c.first_name customer_first_name,
c.last_name customer_last_name,
s.first_name staff_first_name,
s.last_name staff_last_name,
amount,
payment_date
FROM customer c
INNER JOIN payment p
ON p.customer_id = c.customer_id
INNER JOIN staff s
ON p.staff_id = s.staff_id
ORDER BY payment_date;
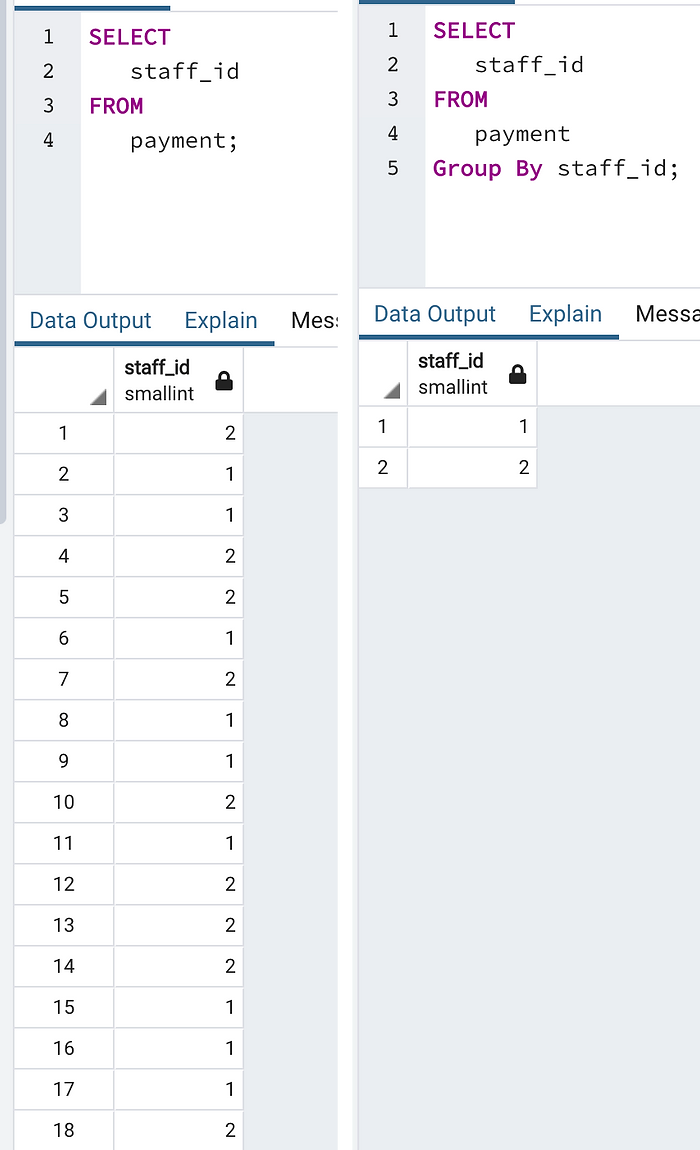
+ GROUP BY:
We’re going to group value from Select statement. We can use Group By. In the simple database, We can group data of payment table by customer_id, staff_id.
Example:
SELECT
staff_id
FROM
payment
Group By staff_id;
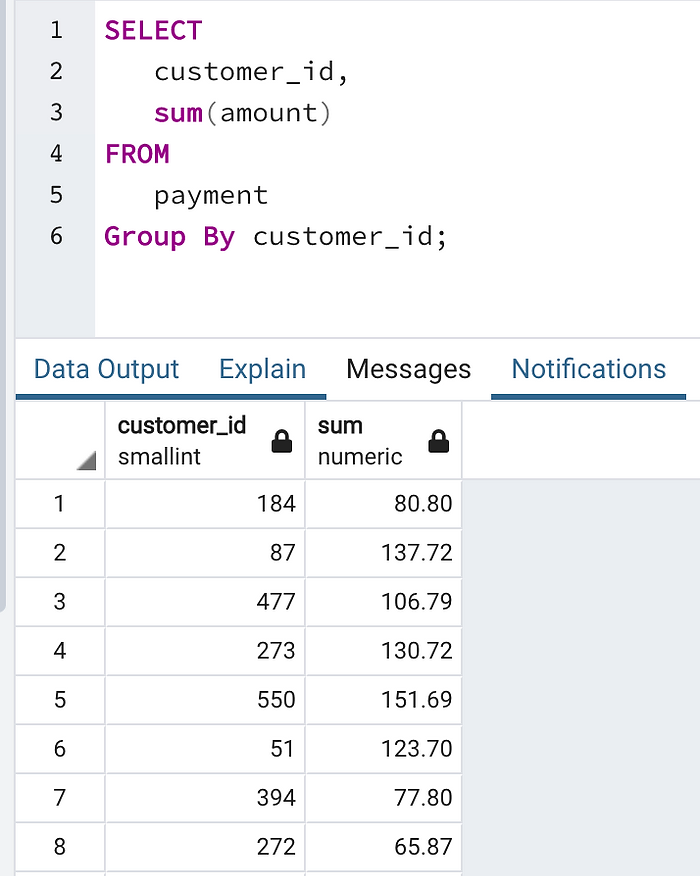
Example - GROUP BY with SUM() function:
In some cases, we expect to get the sum of payment amount that each customer has been paid.
Group by with Sum function we can do that:
SELECT
customer_id,
SUM (amount)
FROM
payment
GROUP BY
customer_id;
+ INSERT STATEMENT
In order to insert a new row into a table, we can use INSERT statement with this syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name(column1, column2, …) VALUES (value1, value2, …);
We can use Insert statement to insert 1 new record into staff, In the simple database, we have 2 staff records, we will insert 3rd staff with this command
INSERT INTO public.staff (staff_id, first_name, last_name, address_id, email, store_id, active, username, password, last_update, picture) VALUES ('3','Jack','Son','5','Jack.Son@sakilastaff.com','2','t','Jack','8cb2237d0679ca88db6464eac60da96345513964','2021-05-16 16:13:11.79328','');
++ Delete:
Syntax for Delete statement:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
We can use this statement to delete the new record that we insert before
Delete public.staff where staff_id = 3;
INCLUSION
We just learn together basic SQL commands / statement for a QA. They are very useful when we do testing.
-
SEL:ECT
-
INNER JOIN
-
GROUP BY
-
INSERT
+DELETE
— Copyright 2024 —
 SQL for QA - Full Course
SQL for QA - Full Course